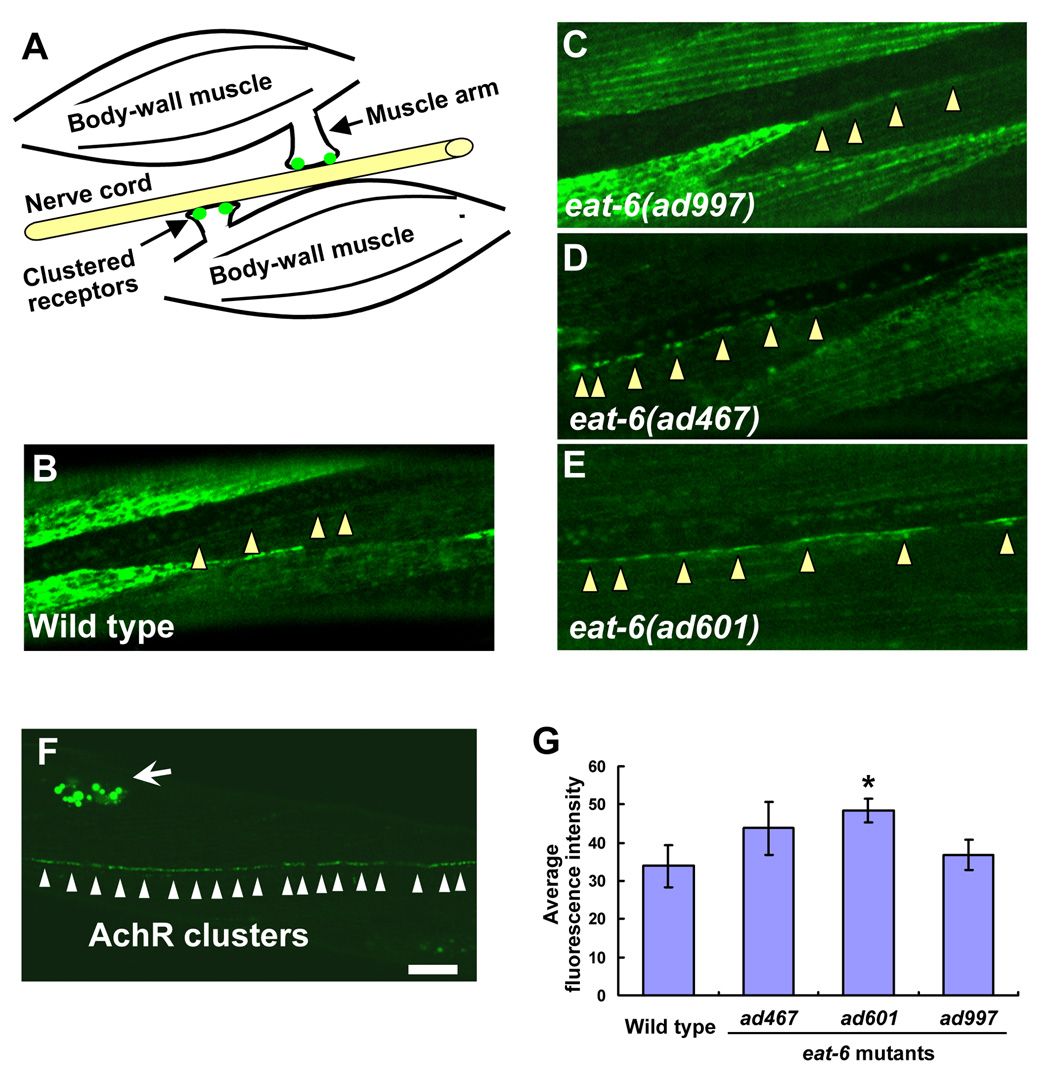
Figure 3. Increased expression and localization of levamisole-sensitive nAchRs in the eat-6 mutants.
(A) Schematic drawing of a C. elegans NMJ. Each muscle cell in the left or right ventral muscle quadrant innervates muscle arms and forms synapses on the axon of motor neurons. Clustered receptors are localized on the distal part of the muscle arms. (B – E) Localization patterns of UNC-29:: GFP fusion protein at NMJs along the ventral nerve cord. (B) Wild type. (C) eat-6(ad997). (D) eat-6(ad467). (E) eat-6(ad601). Arrowheads indicate NMJs along the ventral nerve cord. Note the strong GFP signal in the ad467 and ad601 animals compared to undetectable signal in the wild-type and ad997 animals. (F) A staining pattern for LEV-1:: 3xHA fusion protein using fluorescently-labeled anti-HA antibodies in the wild-type animal. Six hours after the injection of the antibody, puncta were observed along the ventral nerve cord. Excess antibodies were removed by coelomocytic endocytosis (arrow). (G) Average fluorescence intensity in the wild-type and mutant animals (n = 8–12). * P < 0.05, compared to the wild type, two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-test. Error bars indicate SEM. Scale bar, 10 µm.