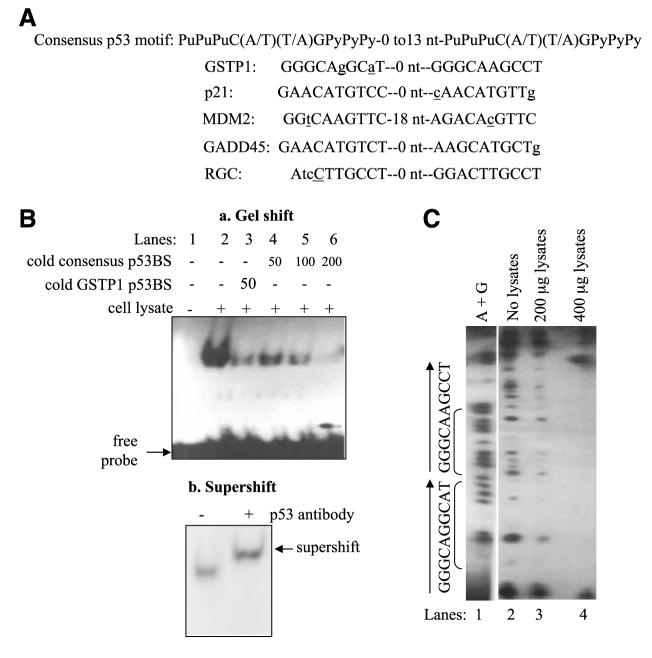
FIGURE 1.
Identification and functional characterization of the GSTP1 p53-binding sites. A. Comparison of the p53-binding motif in intron 4 of the GSTP1 gene with consensus p53-binding site (24) and those in known p53-responsive genes. Spacer nucleotides between two p53 half-sites are indicated. Nucleotides that do not match the consensus p53-binding motifs are in lower case and underlined. B. Binding of wild-type p53 protein to the GSTP1 p53-binding motif. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay was done with oligonucleotides corresponding to the GSTP1 p53-binding motif and protein extracts from Sk-Ala cells containing wild-type p53. a, lane 1, 32P-labeled GSTP1 p53 motif with no protein extract; lane 2, 32P-labeled probe and p53-containing protein extracts; lane 3, competition with 50-fold excess of unlabeled GSTP1 p53 motif probe; lanes 4 to 6, competition experiments with 50-, 100-, and 200-fold excess of unlabeled (cold) consensus binding sites (24). b, supershift of p53 protein bound to GSTP1-binding motif. The p53 monoclonal antibody DO-1 was added to protein extract from Sk-Ala cells preincubated with the 32P-end—labeled probe. Arrow, supershifted band. C. DNase I footprinting analysis of wild-type p53 protein binding to the GSTP1 p53 motif. Wild-type p53 protein extracts from Sk-Ala cells were used in these studies. Lane 1, Maxam-Gilbert sequencing of the nucleotide sequence (A+G) of the footprint probe; lane 2, sequence of the GSTP1 p53 motif without protein extract; lanes 3 and 4, contained 200 and 400 μg of p53-containing protein from Sk-Ala cells, respectively. Brackets, the sequence of the protected region corresponds to the GSTP1 p53-binding motif.