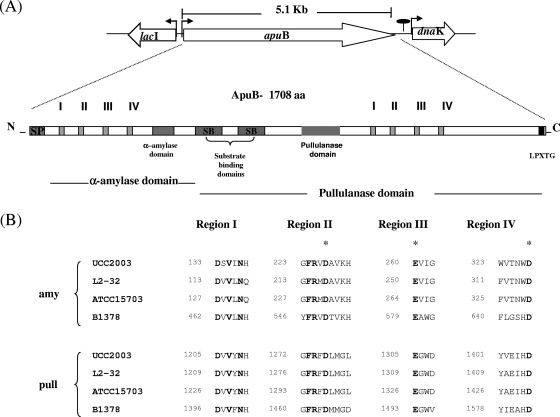
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic representation of apuB and surrounding genes. ApuB is encoded by a single open reading frame of 5,127 bp, producing a protein of 1,708 amino acids which includes a signal sequence of 34 amino acids (SP). The α-amylase and pullulanase domains are located in the amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal portion, respectively. Within the protein, four regions highly conserved in α-amylase-like proteins were identified. In addition, specific α-amylase and pullulanase domains were identified. Two copies of a domain (SB) rich in aromatic amino acids were identified between the α-amylase and pullulanase domains. These domains are believed to be involved in substrate binding. aa, amino acids. (B) Two copies of the four regions highly conserved among α-amylases, pullulanases, and amylopullulanases were identified in ApuB and in amylopullulanases from B. adolescentis strains L2-32 and ATCC 15703. The amino acids in bold are conserved among all amylolytic enzymes, while the putative catalytic amino acids are denoted by asterisks. The sequence of the well-characterized alkaline amylopullulanase from Bacillus sp. KSM-1378 (GenBank accession no. D78258) is included.