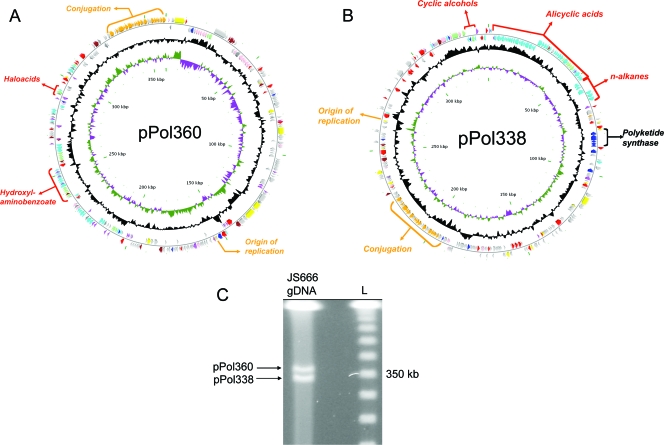
FIG. 2.
(A) The 360-kb plasmid pPol360 of Polaromonas sp. strain JS666. (B) The 338-kb plasmid pPol338 of Polaromonas sp. strain JS666. Approximate locations of important metabolic gene clusters, plasmid replication, and conjugation genes are indicated outside of the first circle, which depicts coding regions on the plus strand colored by functional category: plasmid transfer (orange); plasmid replication and maintenance (yellow); transport (light green); DNA replication, recombination, and repair (red); metabolism (cyan); biosynthesis (dark blue); regulators (purple); cell envelope and membrane biogenesis (pink); general function prediction (brown); conserved hypothetical (dark gray); and no COG (light gray). Moving toward the center, the second circle depicts coding regions on the minus strand (with the same color scheme as the plus strand). The third circle shows G+C content (deviation from average), and the fourth circle G+C skew in purple and olive. The scale (in kbp) is indicated on the innermost circle. The base pair numbering for both plasmids begins near the putative origins of replication (i.e., repB [Bpro_5513] in pPol338 and trfA [Bpro_5045] in pPol360). (C) PFGE of genomic DNA (gDNA) from Polaromonas sp. strain JS666 depicting the presence of two extrachromosomal genetic elements. L, 50-kb lambda ladder.