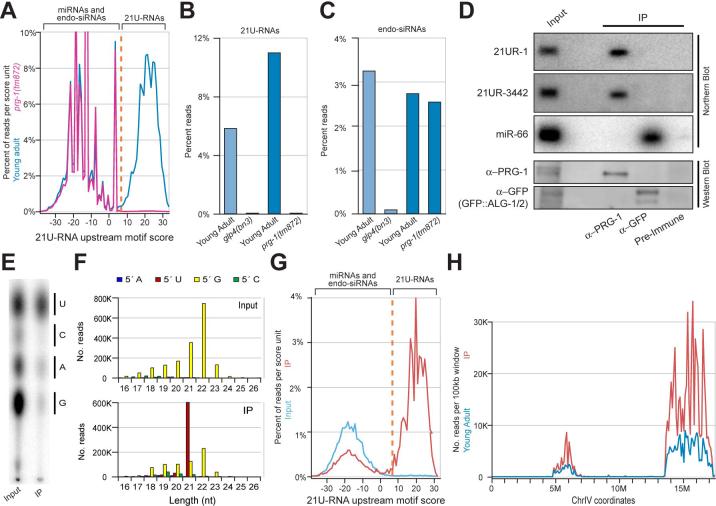
Figure 4. PRG-1 interacts with and is required for the accumulation of all 21URNAs.
(A) The frequency of 21nt RNA reads from wild-type young adults (blue) and prg-1(tm872) young adult (pink) versus upstream motif score. A cut-off score of 7 (orange) was used to define the 21U-RNA population. (B) 21U-RNAs are absent in glp-4(bn2) and prg-1(tm872) mutant worms. Percent reads from each library with 21U-RNA identity are shown. Histogram bars colored as in Figure 2C. (C) Endogenous siRNAs are absent in glp-4(bn2) but not prg-1(tm872) mutant worms. Percent reads with 5′ G nucleotides and complete antisense overlap with coding exons (Ambros et al., 2003) are shown. Histogram bars colored as in Figure 2C. (D) IP/Northern blot analysis of small RNAs in PRG-1 and GFP::ALG1/2 complexes. Immunoprecipitations were performed on lysates prepared from an otherwise wild-type transgenic strain carrying GFP-tagged ALG-1 and ALG-2. The top panels are Northern blots probed for associated small RNAs. The lower panels are Western blots probed as indicated. (E) Thin Layer Chromatography analysis of the first nucleotide of the small RNA population that co-immunoprecipitates with the PRG-1 protein. Bars show where the single nucleotides migrate. (F) The length and 5′ nucleotide distribution of reads from the Input (top) and PRG-1 co-IP (bottom) libraries. (G) The frequency of 21nt RNA reads from the Input (blue) and PRG-1 co-IP (red) libraries versus upstream motif score. Plotted as in Figure 4B. (H) The distribution of 21U-RNA reads from the PRG-1 co-IP library (red) versus the young adult wild-type library prepared with T4 RNA ligase 1 (see methods; blue). Reads were classified as 21U-RNAs by their motif scores and normalized read counts were summed for each non-overlapping 100kb bin.