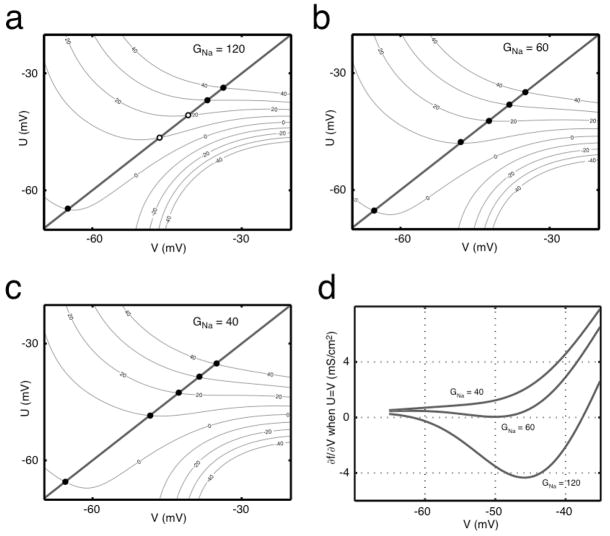
Figure 5. V nullclines described by f(U,V) = I.
(a) The surface of Eq. (7) is plotted as a contour in current I (μA/cm2) for the conductances (GNa, GK, GLeak) = (120, 36, 0.3). (b) f(U,V) for (GNa, GK, GLeak) = (60, 36, 0.3), which is very close to the boundary. (c) f(U,V) for (GNa, GK, GLeak) = (40, 36, 0.3). Fixed points fall on the line U=V, where stable and unstable fixed points are represented by closed and open circles, respectively. (d) The partial derivative of f(U,V) with respect to V evaluated for U=V for three sets of conductances. The top (GNa = 120 mS/cm2) and bottom (GNa = 40 mS/cm2) traces represent approximately integrating and approximately differentiating neurons, respectively. The middle (GNa = 60 mS/cm2) trace lies approximately at the boundary between the two regimes. For this AK model, (GK, GLeak) were (36, 0.3) mS/cm2.