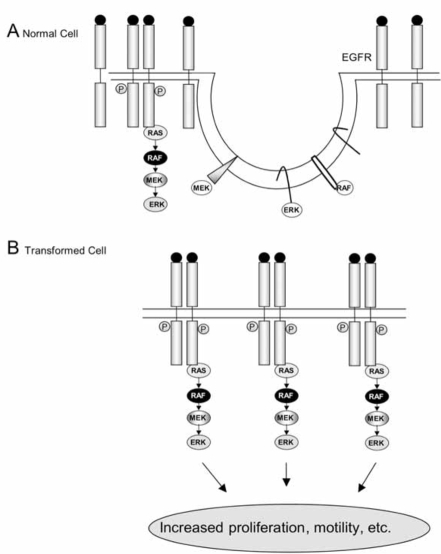
Fig. (3).
Model for the role of caveolae in cellular transformation. A) In a normal cell, caveolin (hairpin structures) binds and inhibits receptors e.g., the EGFR and components of the MAPK cascade. B) In a transformed cell with low caveolin levels, more growth factor receptors and components of the MAPK cascade are free from the inhibitory effects, and this leads to increased proliferation. For clarity, not all components of the MAPK cascade are shown. Inactive molecules are shown as open ovals, whereas active molecules are depicted as filled ovals; EGF = epidermal growth factor; Erk = extracellular signal-regulated kinase.