Figure 6.
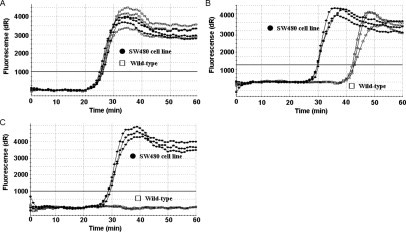
Comparison of PNA and conventional CP for suppression of background amplification in detection of KRAS mutations at codon 12. Shown are 40 ng of SW480 cell line DNA (GTT, homozygous) as a mutant template (closed circles) and 40 ng of wild-type human genomic DNA (GGT, homozygous) as a wild-type template (open squares). A: SMAP-2 amplification without the CP and PNA shows that amplifications of both wild-type and mutant allele were detected at the same time (∼25 minutes). B: SMAP-2 amplification with a conventional CP cannot suppress wild-type allele amplification completely. In this study, 28 different CP sequence designs were tested. Typical data are shown. C: SMAP-2 amplification with a PNA-clamp competitive probe could suppress wild-type allele background amplification completely.
