Figure 3.
The Predicted MPC Protein Has Homology to the C-Terminal Domain of Poly(A) Binding Proteins and Can Bind CID Proteins That Also Interact with a Full-Length Arabidopsis PABP.
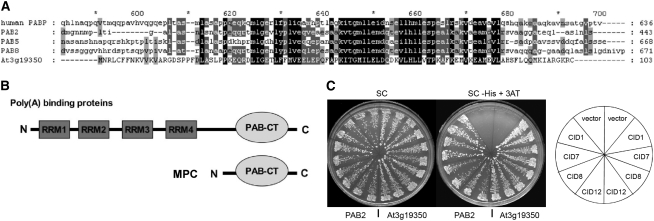
(A) Alignment of the complete predicted MPC (At3g19350) protein with the C-terminal domains of the major human PABP and three Arabidopsis PABPs. Conserved amino acid residues are shaded.
(B) The structure of MPC compared with a typical PABP.
(C) A yeast two-hybrid assay indicates that PAM2-containing fragments of CID1, CID7, CID8, or CID12 interact with MPC in a similar manner as with PAB2. The plates show streaks of two representative yeast colonies for each one of the two-hybrid interactions tested. In the left half of the plate are the interaction with PAB2 and in the right half with MPC (At3g19350). Colonies were streaked on synthetic complete (SC) medium to select for both two-hybrid clones and on SC supplemented with 5 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (SC-His + 3AT) to assess the interaction. The position of the interactions in the plate is indicated on the slices of the diagram to the right of the figure; vector represents the empty cloning vector.