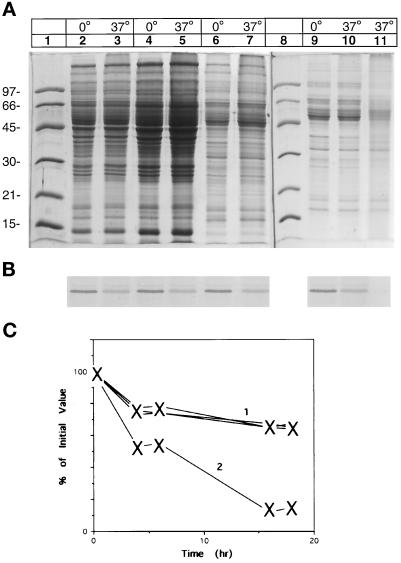
Figure 5.
Proteolysis of desaturase in the high-salt–washed microsomes cannot be reconstituted by the addition of cytosol or high-salt wash supernatant but can be restored by supplementation with lipids and cytochrome b5 reductase. Lanes 2 and 3, high-salt–washed microsomes (5 μg) were supplemented with an aliquot of cytosol (10 μg). Lanes 4 and 5, high-salt–washed microsomes supplemented with an aliquot of concentrated cytosol (20 μg) or concentrated high-salt wash (7 μg), lanes 6 and 7. Lane 9, high-salt–washed microsomes; lane 10, high-salt–washed microsomes with added lipids; lane 11, high-salt–washed microsomes with added lipids and cytochrome b5 reductase. Samples of the incubation mixtures were run on duplicate gels. (A) Coomassie Blue-stained gel. (B) Immunoblot of the above gel with antidesaturase antibody. (C) Estimated time course of the degradation of the desaturase. Aliquots of the various fractions were incubated and quantitated as described in the legend of Figure 4C. Curve 1, high-salt–washed microsomes supplemented with cytosol, or aliquot containing high-salt wash. Curve 2, high-salt–washed microsomes with added components essential for the reconstitution of the desaturase reaction. The amount of desaturase was determined by densitometry and is expressed as a percentage of the amount present at the start of the experiment, which is set to 100%.