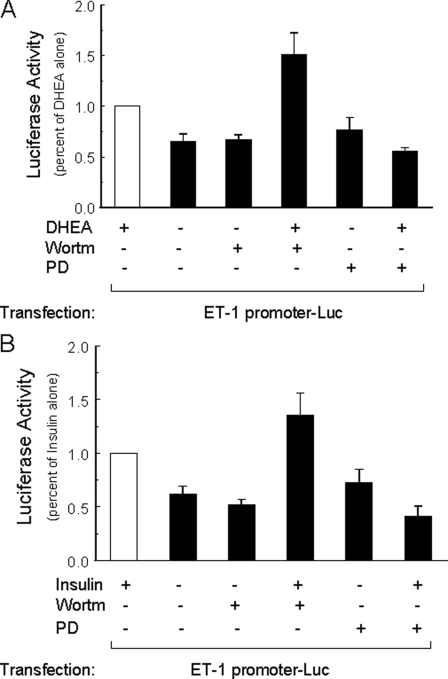
FIGURE 7.
Activation of ET-1 promoter in response to DHEA or insulin treatment was augmented by PI 3-kinase blockade and inhibited by MAPK blockade. BAECs grown in 24-well plates were transfected with ET-1 promoter luciferase reporter and renilla luciferase (internal control). One day later cells were serum-starved overnight and then treated for 8 h with vehicle, DHEA (100 nm), or insulin (100 nm) without or with wortmannin (100 nm), PD98059 (12.5 μm). Luciferase activity in each group was normalized to that in the group treated with DHEA alone (panel A, mean ± S.E. of eight independent experiments in triplicate) or insulin alone (panel B, mean ± S.E. of eight independent experiments in triplicate). When compared with cells treated with vehicle alone, ET-1 promoter activity was significantly increased in cells treated with either DHEA (panel A, p < 0.001) or insulin (panel B, p < 0.001). When compared with cells treated with DHEA or insulin alone, ET-1 promoter activity was further increased in cells co-treated with wortmannin (panel A, p < 0.03; panel B, p = 0.05) and inhibited in cells co-treated with PD98059 (panel A and B, p < 0.0001).