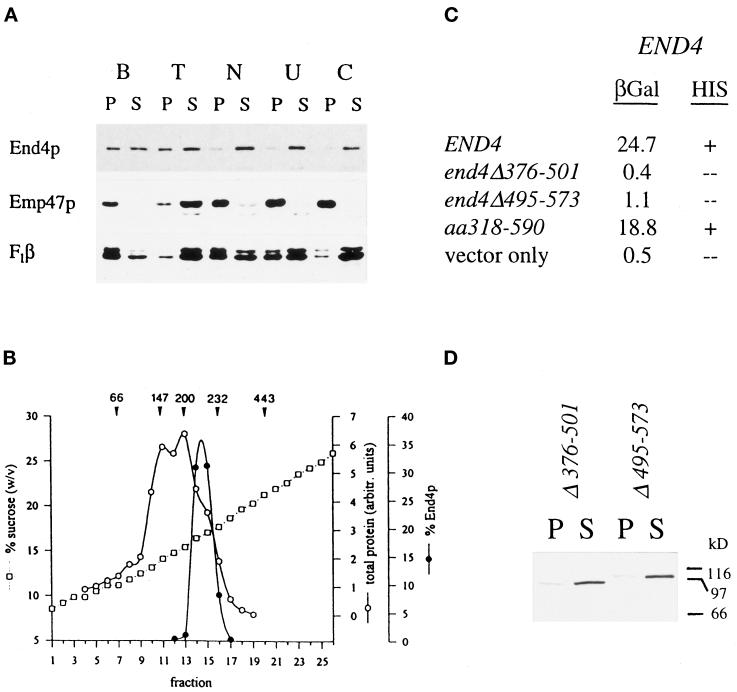
Figure 2.
Coiled-coil domain of End4p mediates complex formation. (A) Wild-type cell extracts were incubated on ice for 1 h in 1% Triton X-100 (lane T), 0.5 M NaCl (lane N), 2.5 M urea (lane U), or 0.1 M carbonate, pH 11.5 (lane C) or were mock treated with lysis buffer (lane B). After high-speed centrifugation, equivalent volumes of pellets (lanes P) and supernatants (lanes S) were analyzed for End4p and control proteins by immunodetection. (B) Wild-type cell lysates were fractionated on linear 9–30% sucrose gradients. Fractions were collected from the top (fraction 1) and End4p content was quantified by Western blotting. Arrowheads indicate the position of the peaks of marker proteins; numbers are given in kDa. (C) Wild-type END4 as well as mutant end4 alleles were fused in-frame to the gal4 transcription-activation domain. These fusion constructs were tested in the two-hybrid system for interaction with the wild-type END4 gene fused to the LexA DNA-binding domain. β-Galactosidase activities of extracts prepared from yeast strain L40 harboring the various combinations of plasmids were measured and expressed as units/milligram of protein. Alternatively, growth on plates lacking histidine was scored to monitor interaction of End4p. (D) Extracts of end4Δ376–501 (RH3395) and end4Δ495–573 (RH3397) mutants were prepared in lysis buffer and processed as described in A. Mutant End4p was visualized in pellets (lanes P) and supernatants (lanes S) by immunodetection.