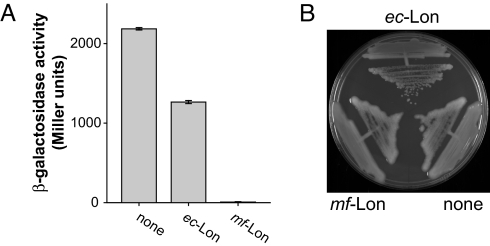
Fig. 1.
Phenotypes of mf-Lon expression in E. coli. (A) E. coli strain MC4100 was transformed with a plasmid expressing an IPTG-inducible β-galactosidase-mf-ssrA fusion protein and a second plasmid expressing either ec-Lon, mf-Lon, or neither enzyme. Intracellular β-galactosidase-mf-ssrA was assayed by enzymatic cleavage of X-Gal as described in Materials and Methods. Values are averages (±1 SD; n = 5). (B) Complementation of the mucoid phenotype of a Δlon strain by ec-Lon but not mf-Lon. E. coli strain JT4000 (MC4100 Δlon) was transformed with plasmids expressing ec-Lon, mf-Lon, or a mock vector, as indicated. Cells were plated on minimal medium (45) agar plates with glycerol (0.4%) as a carbon source and chloramphenicol (10 μg/ml). In both panels, ec-Lon and mf-Lon were expressed at basal levels under control of an l-arabinose promoter (PBAD) without added l-arabinose. Arabinose induction of the expression of either Lon enzyme resulted in growth arrest.