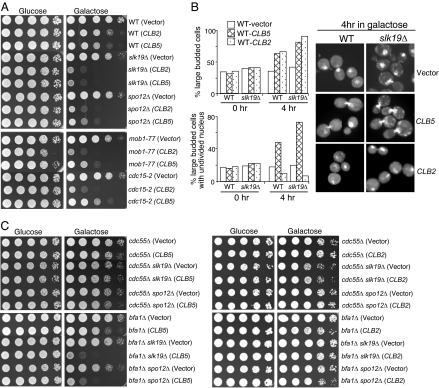
Fig. 3.
The comparison of the toxicity of high levels of Clb2 and Clb5 to FEAR and MEN mutant cells. (A) Overexpression of CLB5 and CLB2 shows differential toxicity to FEAR and MEN mutants. Stationary phase cells with vector, PGAL-CLB2 or PGAL-CLB5 plasmids were 10-fold diluted and spotted onto URA dropout plates containing either glucose or galactose. The plates were scanned after 3-day incubation at room temperature. (B) CLB5 overexpression leads to nuclear division defects. WT and slk19Δ cells with either vectors or PGAL-CLB2, PGAL-CLB5 plasmids were incubated in raffinose medium to midlog phase. Galactose was added into the medium to a final concentration of 2% and cells were collected at 0 and 4 h for the examination of budding index and nuclear division after DAPI staining. The percentage of large budded cells and cells with unseparated nucleus and the nuclear morphology in some representative cells are shown. (C) Hyperactive FEAR, but not MEN, suppresses the toxicity of CLB5 overexpression. Stationary phase cultures with indicated genotypes were tenfold diluted and spotted onto URA dropout plates containing glucose or galactose. The plates were scanned after 3 day incubation at 30°C.