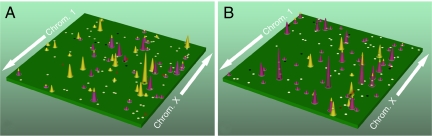
Fig. 2.
Genomic landscape of copy number and nucleotide alterations in two typical cancer samples. A indicates breast cancer alterations, whereas B indicates colorectal cancer alterations. The telomere of the short arm of chromosome 1 is represented in the rear left corner of the green plane and ascending chromosomal positions continue in the direction of the arrow. Chromosomal positions that follow the front edge of the plane are continued at the back edge of the plane of the adjacent row and chromosomes are appended end to end. Peaks indicate the 60 highest-ranking candidate cancer genes for each tumor type, with peak heights reflecting the passenger probability scores. The yellow peaks correspond to genes that are altered by copy number changes, whereas those altered only by point mutations are purple. The dots represent genes that were altered by copy number changes (red squares) or point mutations (white circles) in the B9C breast or Mx27 colorectal tumor samples. Altered genes participating in significant gene groups or pathways (Table S6) are indicated as black circles or squares.