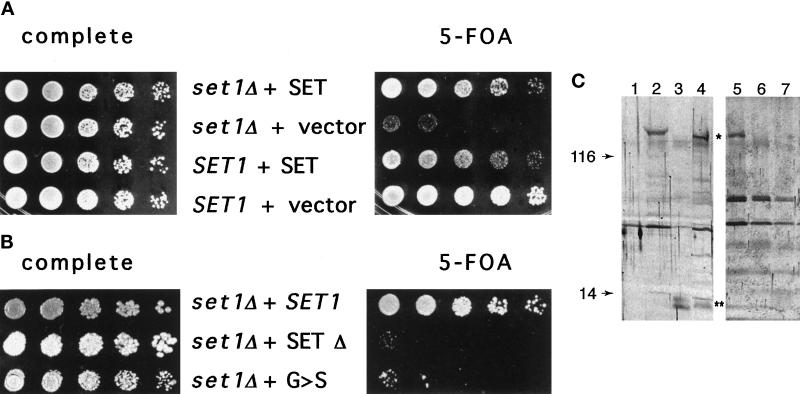
Figure 6.
The SET domain functions in telomeric silencing. (A) The SET domain alone rescues the set1 telomeric silencing defect. SET1 and set1 mutant strains were transformed with plasmids containing the 130 amino acid SET domain (LPY2461, LPY2462) or a control vector (LPY2463, LPY2460). When telomeric silencing of a URA3 reporter gene was evaluated using the 5-FOA sensitivity assay, expression of the SET domain alone restored silencing to the set1 mutants. (B) Telomeric silencing assays were performed with set1 mutants bearing either wild-type SET1 (LPY2456), a deletion encompassing the SET domain (LPY2457), or a set1 point mutation that alters glycine951 to serine (LPY2458). Strains bearing the point mutation show minimal growth on 5-FOA and the SET deletion mutant is completely unable to grow on 5-FOA, demonstrating that mutation of the SET domain reduces or destroys telomeric silencing, depending on the mutation. (C) Immunoblot analysis of protein extracts from a set1 mutant strain transformed with pTRP vector alone (lane 1, LPY2460) do not contain the 135-kDa band seen in the same set1 strain transformed with pTRP bearing the full-length SET1 gene (lane 2, asterisk, LPY2459). The set1 strain transformed with a plasmid encoding the SET domain alone shows an immunoreactive doublet of 13–14 kDa (lane 3, double asterisk, LPY2462). A SET1 strain with the SET-domain-only plasmid has immunoreactive species at 135 kDa and the 13- to the 14-kDa doublet (lane 4, LPY2461). The set1 mutant strains transformed with wild-type SET1 (lane 5, LPY2456), the set1-G951S allele (lane 6, LPY2458), or the set1 SET domain deletion allele (lane 7, LPY2457) are shown. Normal Set1 protein is observed in lane 5, whereas little or no immunoreactive material is seen with the mutant constructs. Additional nonspecific bands of variable molecular mass and intensity are seen in lanes 1–7. Molecular mass markers in kilodaltons are shown at left.