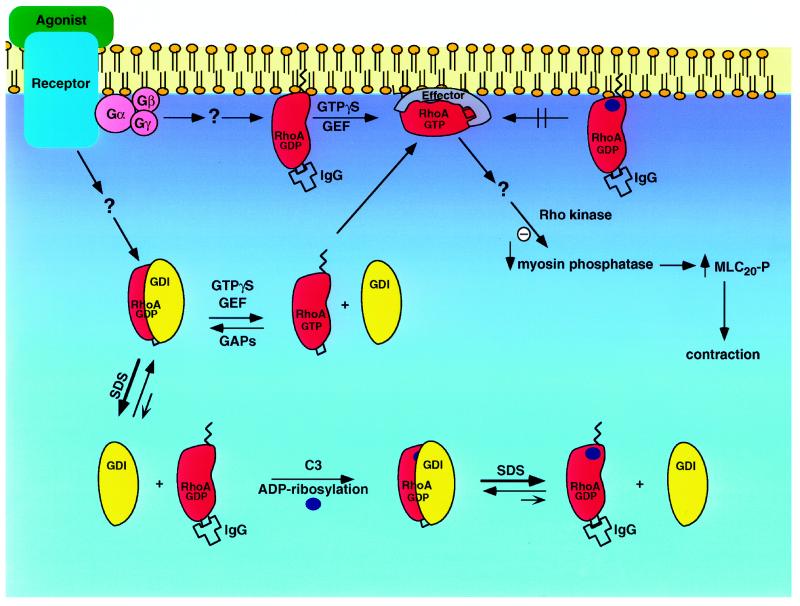
Figure 8.
Steps of RhoA activation and of the inhibition of RhoA activity by ADP ribosylation of its Asn 41 residue. The alignment of RhoA and rhoGDI in the heterodimer formed by the two proteins, while schematic, is based on combining the results of ADP ribosylation and immunoprecipitation of RhoA with the crystal and nuclear magnetic resonance structures of the respective proteins (Gosser et al., 1997; Keep et al., 1997; Wei et al., 1997). ADP ribosylation of RhoA is indicated by dark blue circles; the insert loop (Wei et al., 1997), the region of the epitope to which the immunoprecipitating antibody was generated, is indicated by a square; and the zigzag line represents the flexible, prenylated C terminus of RhoA that is thought to be largely responsible for membrane binding. The main phenomena illustrated are: 1) in unstimulated smooth muscle RhoA is present mainly as a cytosolic complex with rhoGDI that can be neither immunoprecipitated nor ADP ribosylated, and a small fraction of inactive, membrane-associated RhoA that can be ADP ribosylated and immunoprecipitated. 2) Dissociation of the RhoA–rhoGDI complex, accelerated by SDS, renders it available for both immunoprecipitation and ADP ribosylation. 3) Activation of RhoA with GTPγS (or GTP plus an agonist) causes translocation of RhoA to the membrane and activates already membrane-associated, inactive RhoA, making both the ADP-ribosylation site (Asn 41) and the immunoprecipitating epitope unaccessible, due to the association of RhoA with a putative effector and/or other membrane structure. 4) Treatment with DC3B for 48 h results in ADP ribosylation of both the cytosolic rhoGDI-complex and membrane-associated RhoA, and prevents the association of RhoA with the membrane-bound effector, as indicated by its immunoprecipitability after exposure to GTPγS. The site of dissociation of the heterodimer, whether within the cytosol or during transient association with the membrane, is not known. Association of activated RhoA with its effector results in inhibition of smooth muscle myosin phosphatase, increased phosphorylation of the regulatory myosin light chain (MLC20), and contraction. GDI, rhoGDI; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; GAP, GTPase activating protein.