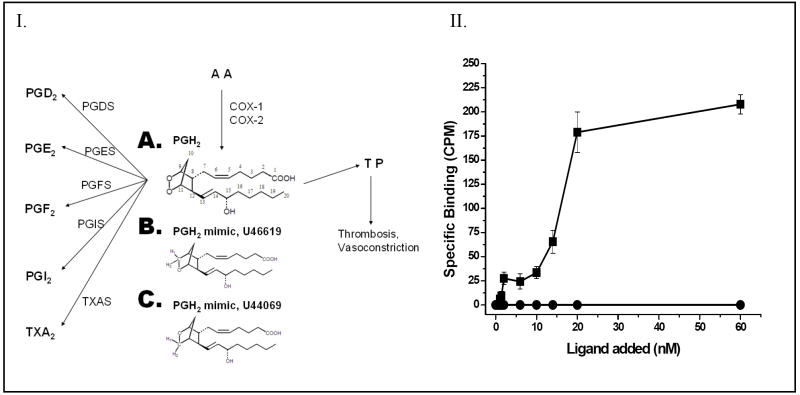
Figure 1.
Panel I. The multiple target proteins of PGH2 synthesized from arachidonic acid (AA) through the COX pathway. The COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes convert AA to PGH2 (A), which serves as a common substrate for COX-downstream synthases including PGDS, PGES, PGFS, PGIS and TXAS, and also serves as an agonist for the TP. The chemical structures of the PGH2 mimics, U46619 (A), and U44069 (B) are also shown. Panel II. The specific ligand binding activity of the purified TP from Sf9 cells. The purified TP protein (■) in PBS was incubated with increasing amounts (0 to 60 nM) of the ligand, [3H]U46619. Unlabeled U46619 (1μM) was added to the Sf9 cells as a negative control (●) before the radio-labeled ligand was added. The results are representative data from three assays (n=3) and are shown as means ± the standard error.