Figure 1.
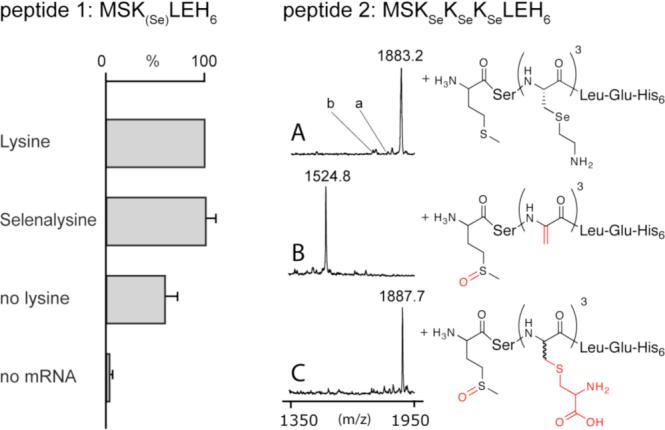
Selenalysine incorporation assay. Left: The efficiency of peptide 1 production was determined by scintillation counting of specific 35S-Met activity. The bars represent the average of three independent measurements and the averaged value for the lysine containing reactions (35 ± 3 pmol) was set to 100 %. Control translation reactions without supplemented lysine (no lysine) show a significant background due to the presence of contaminating lysine in the translation mixture. Right: MALDI-TOF analysis of the peptide 2 after translation (A, mcalc. = 1883.6 Da), oxidative elimination (B, mcalc. = 1524.6 Da), and Michael addition of L-cysteine (C, mcalc. = 1887.7 Da). Signals consistent with the production of peptides containing one (a) or two (b) lysines are indicated. To improve detectability by MALDI-TOF, peptides 1 and 2 were produced as the free N-terminal amine by omission of the formyl donor (10-formyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolic acid ) necessary for formylation of methionyl-tRNA.
