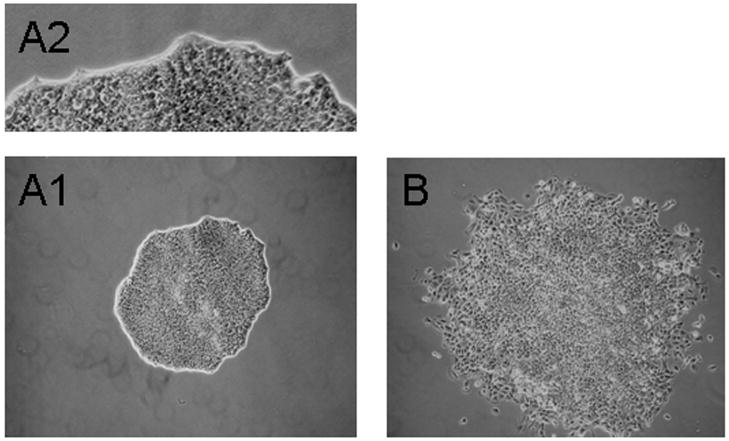
Fig. 1.
Clonal morphology of “parental” P19 and variant P19-SI cells. Parental P19 cells were plated at clonal density (see Experimental Procedures) and grown for 5 days. The clones were located, marked and observed using an inverted, phase contrast microscope. The majority of clones (>95%) displayed a “tight” morphology (A1 and A2), while the morphology of the minority clone population was less compact (B). When clones of the latter type were expanded, the cells were found to be “self-inducing” to a cardiac phenotype (see text). The images in A1 and B are the same magnification.