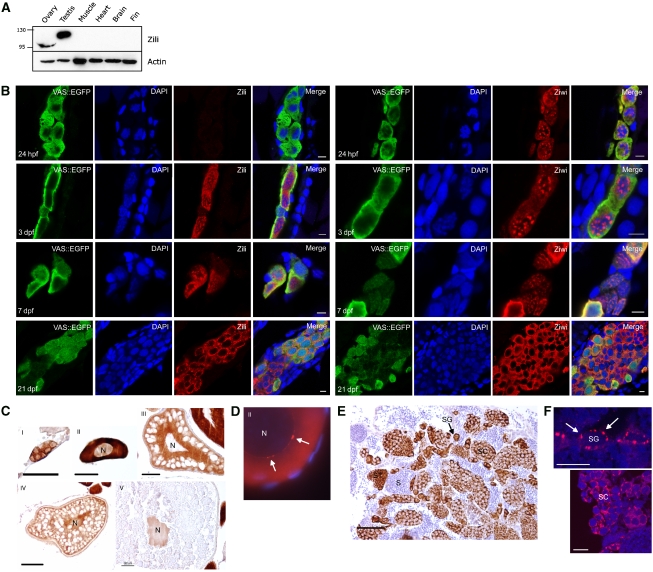
Figure 1.
Zili is a nucleocytoplasmic protein. (A) Western blot showing specific expression of Zili in testis and ovary. The migration path of the Zili protein is distorted by highly abundant yolk proteins, resulting in a lower band for Zili in ovary than testis. (B) At 24 h post-fertilization (hpf), Zili protein cannot be detected in PGCs, whereas Ziwi protein is maternally provided and localizes to perinuclear granules. At 3 days post-fertilization (dpf), Zili protein is present in the nucleus of PGCs, as well as in the cytoplasm. From 7 dpf onwards, Zili protein starts localizing to the cytoplasm, whereas at this point, Ziwi protein exits the perinuclear granules and becomes diffuse in the cytoplasm. At 3 weeks post fertilization (wpf), Zili displays a granular distribution in the cytoplasm, whereas Ziwi is diffuse. Scale bar is 5 μm. (C) Zili (brown) in ovary is present in all stages of oogenesis in cytoplasm and/or nucleus (N). Stages of oogenesis are oogonia (I), stage I oocytes (7–140 μm; II), stage II oocytes (140–340 μm; III), stage III oocytes (340–690 μm; IV) and stage IV oocytes (0.69–0.73 mm; V) (Selman et al, 1993). Scale bar ia 50 μm. (D) Zili (red) in granules (white arrows) around the nucleus (N) of stage I oocyte. (E) Zili (brown) in testis is present predominantly in the cytoplasm of all stages of spermatogenesis, except the fully differentiated sperm. Stages of spermatogenesis are spermatogonia (SG), spermatocytes (SC), spermatids (ST) and sperm (S). Scale bar is 50 μm. (F) Zili (red) in granules around the nucleus of spermatogonia (upper panel) and spermatocytes (lower panel). Scale bar is 10 μm.