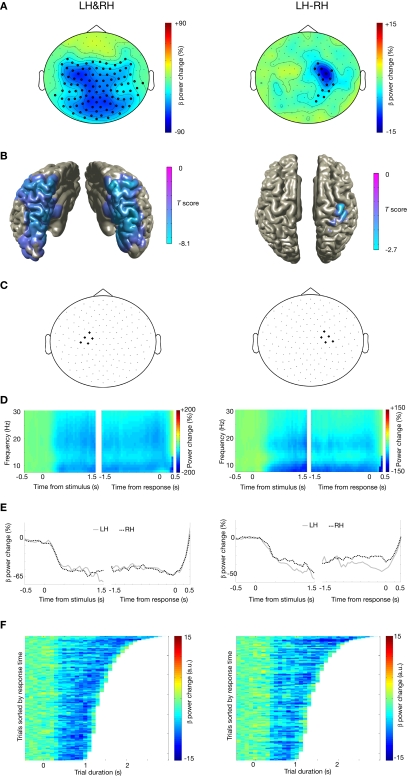
Figure 3.
Beta suppression during motor imagery of left and right hands. (A) Grand average of the topography of changes in power in the beta band (16–24 Hz) between task and baseline (LH & RH, left panel) and between hands (LH-RH, right panel). Dots indicate clusters of significant differences (p < 0.05 corrected for multiple comparisons). (B) Source reconstruction of the changes in power in the beta band between task and baseline (left panel) and between hands (right panel). The power of the source representation is thresholded at half-maximum. (C) Outline of a group of sensors overlying left and right motor cortex that were selected for subsequent analysis. (D) Grand-averaged time-frequency representation of power over left motor cortex (left panel) and right motor cortex (right panel). The time-frequency plots have been aligned to the presentation of the visual stimulus (time = 0, left panel) or to the button-press (time = 0, right panel). (E) Grand-averaged power in the beta band, plotted separately for trials showing drawings of left and right hands [LH, RH, respectively; other conventions as in (D)], for the left motor cortex (left panel) and right motor cortex (right panel). (F) Relationship between trial duration and beta suppression. Beta band power for single trials (sorted by reaction time, time = 0 corresponds to visual stimulus presentation) is plotted against trial duration, for one representative subject and for the sensor selections as outlined in (C). Power values were smoothed over 10 trials windows.