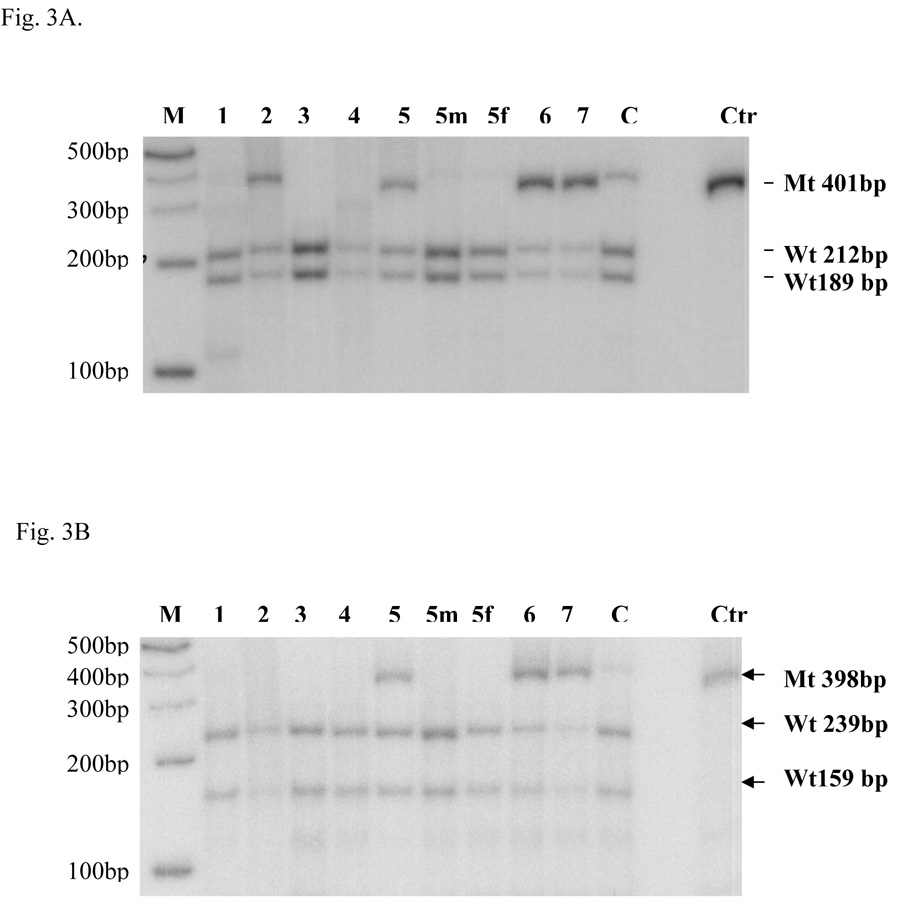
Fig. 3. Quantitative PCR-RFLP.
Quantitative PCR-RFLP was done as described in the Materials and Methods section. Molecular weight markers and patients’ codes are indicated on the top part of the figure. The marker ladder is spaced 100bp apart. 5m and 5f are the mother and father of patient 5. C is a carrier control and Ctr is the undigested control. A. The PCR mutant fragment (Mt) NE3-NE4 (401bp) with substitution c. [1892G>A] could not be digested by Msp I, whereas the wild-type DNA (Wt) NE3-NE4 fragment could be cut into two fragments (189bp and 212bp) as shown by an arrow head on the right side. B. The CO1-CO2 (398bp) mutant fragment (Mt) containing c. [2540C>T] could not be cut by Fnu4H I, whereas the wild-type fragment(Wt) could be cut into two fragments (239 bp and 159bp) as shown by the arrow head on the right side.