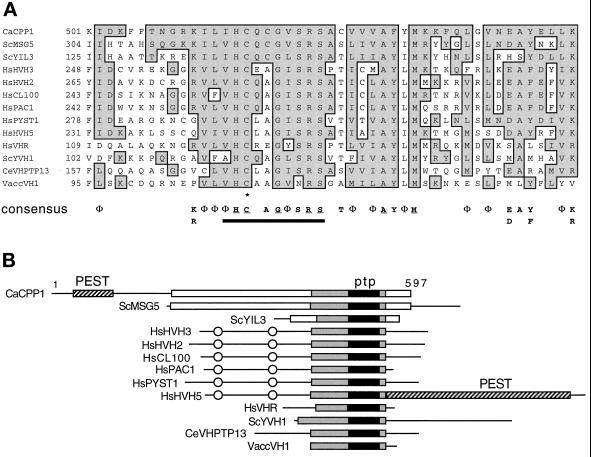
Figure 1.
Structural similarity of CPP1 with VH1 family phosphatases. (A) Similarity of the CPP1 amino acid sequence to a conserved region surrounding the active-site signature sequence of the VH1 family phosphatases. Aligned sequences are C. albicans (Ca) CPP1, S. cerevisiae (Sc) MSG5 (Doi et al., 1994), YIL3 (SWISS-PROT P40558, YIL003W, putative phosphatase), and YVH1 (Guan et al., 1992), human (Hs) HVH3 (Kwak and Dixon, 1995), HVH2 (Guan and Butch, 1995), CL100 (MKP1) (Alessi et al., 1993), PAC1 (Rohan et al., 1993), PYST1 (Groom et al., 1996), HVH5 (Martell et al., 1995), VHR (Ishibashi et al., 1992), Chlamydomonas eugametos (Ce) VHPTP13 (Haring et al., 1995), and Vaccinia (Vacc) VH1 (Guan et al., 1991). Conserved residues (ILVM =Φ; KR; ED; NQ; YF) and identical residues present in the CPP1 polypeptide and one or more of the other polypeptides are boxed and shaded. A VH1 family consensus is presented below the alignment for residues present in 8 or more of the 13 sequences. Residues identical in all 13 sequences are underlined. The PTP-active site motif is underlined with a black bar and the active site essential cysteine is shown with an asterisk. Numbers at the left of the margin specify the amino acid positions within each polypeptide. (B) Schematic alignment of the VH1 family phosphatases. Black boxes represent the highly conserved active site region (PTP) aligned in A around which the alignment is centered. The gray boxes represent an extended homology region with lower identities between sequences. White boxes represent additional regions of alignment among CPP1, MSG5, and YIL3. PEST sequences are shown. CH2 domains are circled. Numbers indicate the size of the CPP1 polypeptide.