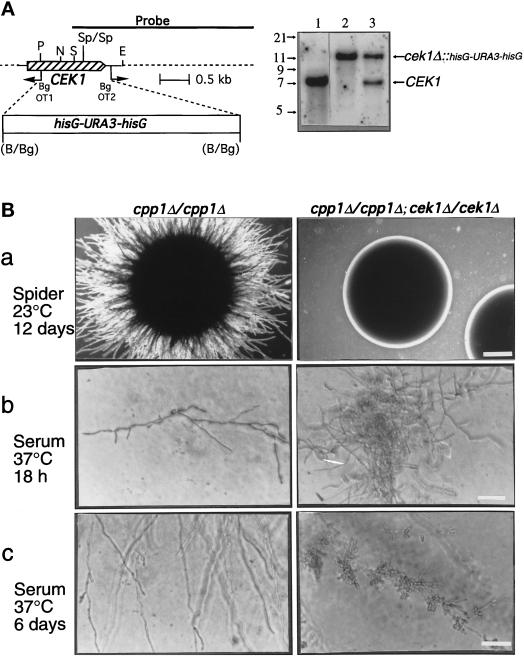
Figure 8.
Construction and phenotypic analysis of cek1/cpp1 double null mutants. (A) Deletion of CEK1 in C. albicans. Left, Deletion strategy and restriction map of the CEK1 gene. PCR with the divergent oligodeoxynucleotides OT1 and OT2 was used to delete a 1.2-kb fragment of the CEK1 gene. A 4.0-kb hisG-URA3-hisG cassette was then inserted. Restriction sites are as follows: B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; P, PstI; S, SacI; N, NsiI; E, EcoRI; and Sp, SpeI. Right, Southern blot analysis of CEK1 disruptions with a 3.2-kb KpnI-SacI fragment containing the CEK1 gene as a probe. Genomic DNA samples were digested with SpeI (absent from the hisG-URA3-hisG cassette) from the following strains: lane 1, CP29–1-7 L4 (ura3/ura3 cpp1Δ::hisG/cpp1Δ::hisG; CEK1/CEK1); lane 2, CP29-1-7 CK14 (ura3/ ura3cpp1Δ::hisG/cpp1Δ::hisG; cek1Δ::hisG-URA3hisG/cek1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG); and lane 3, CP29-1-7 CK13 (ura3/ura3cpp1Δ::hisG/cpp1Δ::hisG; CEK1/cek1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG). Hybridization of a very small part (between the SacI and SpeI sites) of the probe to a 1.4-kb SpeI fragment, present only in the wild-type CEK1 gene, was not detectable in these Southern blots and was not used for diagnostic purposes. (B) Colonies of cpp1 null mutants (cpp1Δ/cpp1Δ) or cpp1/cek1 double null mutants (cpp1Δ/cpp1Δ; cek1Δ/cek1Δ) grown at room temperature (a) on solid Spider medium containing mannitol (2× objective; bar, 1.4 mm) and under physiological conditions (b and c) on solid serum medium (40× objective; bar, 70 μm). In a and b colonies are shown. In c hyphae (and lateral blastospores) from peripheries of mycelial colonies are shown. Our unpublished data demonstrated that the cpp1/cek1 double null mutant phenotypes resembled those of the wild-type strain SC5314.