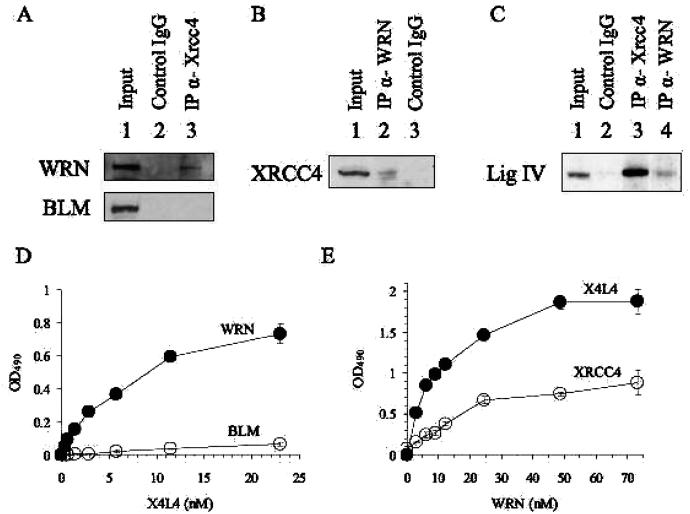
Figure 1.
WRN interacts with X4L4. (A, B, and C) Co-IP assay. Protein complexes were immunoprecipitated from nuclear extracts using control mouse IgG (lane 2 in A) or mouse antibody against XRCC4 (lane 3 in A), using control rabbit IgG (lane 3 in B) or antibody against WRN (lane 2 in B), or using control rabbit IgG (lane 2 in C), rabbit antibody against XRCC4 (lane 3 in C), or rabbit antibody against WRN (lane 4 in C). Proteins immunoprecipitated from HeLa cell nuclear extracts were analyzed by Western blot analysis with rabbit antibody against WRN (upper panel in A) and BLM (lower panel in A), with mouse antibody against XRCC4 (B), or with rabbit antibody against DNA ligase IV (C). 10% of IP input is shown in lane 1 (A, B, and C). (D) ELISA. Wells were coated with 9 nM WRN (●) or BLM (○) and incubated with increasing concentrations of X4L4 (0.36, 0.72, 1.4, 2.9, 5.8, 12, and 23 nM). Bound X4L4 was detected using mouse anti-XRCC4 antibody. (E) ELISA. Wells were coated with 14.4 nM X4L4 (●) or dimeric XRCC4 (○). Increasing amounts of WRN (3.0, 6.1, 9.2, 12, 24, 49, and 73 nM) was added to the wells. Bound WRN was detected using rabbit polyclonal anti-WRN antibody. Absorbance values were corrected for BSA background and plotted against X4L4 (D) or WRN (E). Values and error bars are the mean of at least two independent experiments.