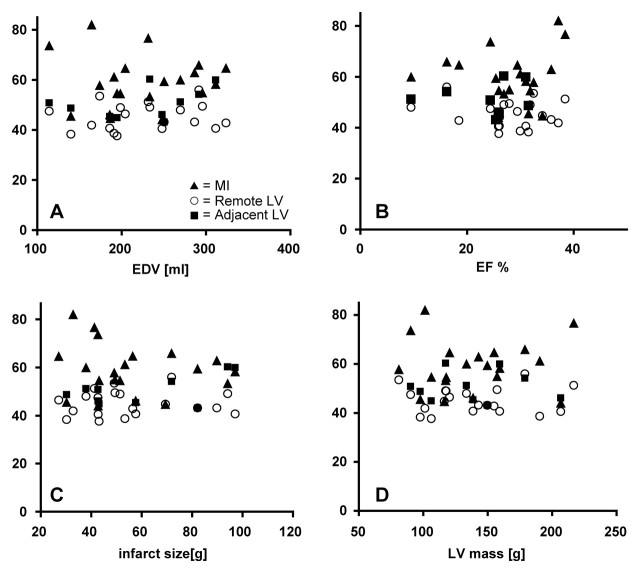
Figure 6:
Graphs show TSC values in MI, adjacent LV, and remote LV, which did not correlate with, A, end-diastolic volume (EDV) (r= −0.002, P > .05), B, ejection fraction (EF) (r= −0.095, P > .05), C, absolute infarct size (r= −0.16, P> .05), or, D, LV mass (r= 0.005, P> .05). Mean TSC values in MI (20 patients), remote noninvolved myocardium (20 patients), and adjacent myocardial regions (11 patients) are shown. Although one might expect the larger infarcts to lead to stress and possibly increased TSC in remote LV tissue or to larger LV mass, or the higher TSC in MI or adjacent tissue to possibly impair cardiac function (as expressed by ejection fraction), no such correlations were apparent from our data.