Abstract
Conjugate vaccines were prepared in an attempt to protect pigs against swine pleuropneumonia induced by Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (SPAP). Two subunit conjugates were prepared by coupling the A. pleuropneumoniae 4074 serotype 1 capsular polysaccharide (CP) to the hemolysin protein (HP) and the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to the HP. Adipic acid dihydrazide was used as a spacer to facilitate the conjugation in a carbodiimide-mediated reaction. The CP and the LPS were found to be covalently coupled to the HP in the conjugates as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and detergent gel chromatography analyses. Following a booster vaccination, pigs exhibited significantly high (P less than 0.05) immunoglobulin G antibodies against CP, LPS, and HP. The anti-CP and anti-LPS immunoglobulin G antibodies were found to function as opsonins in the phagocytosis of A. pleuropneumoniae by polymorphonuclear leukocytes, whereas antibodies to the HP neutralized the cytotoxic effect of the HP on polymorphonuclear leukocytes. No killing of A. pleuropneumoniae was observed when the effects of the antibodies were tested in the presence of complement. Thus, polysaccharide-protein A. pleuropneumoniae conjugates elicit significant antibody responses against each component of each conjugate, which could be instrumental in protecting swine against SPAP.
Full text
PDF



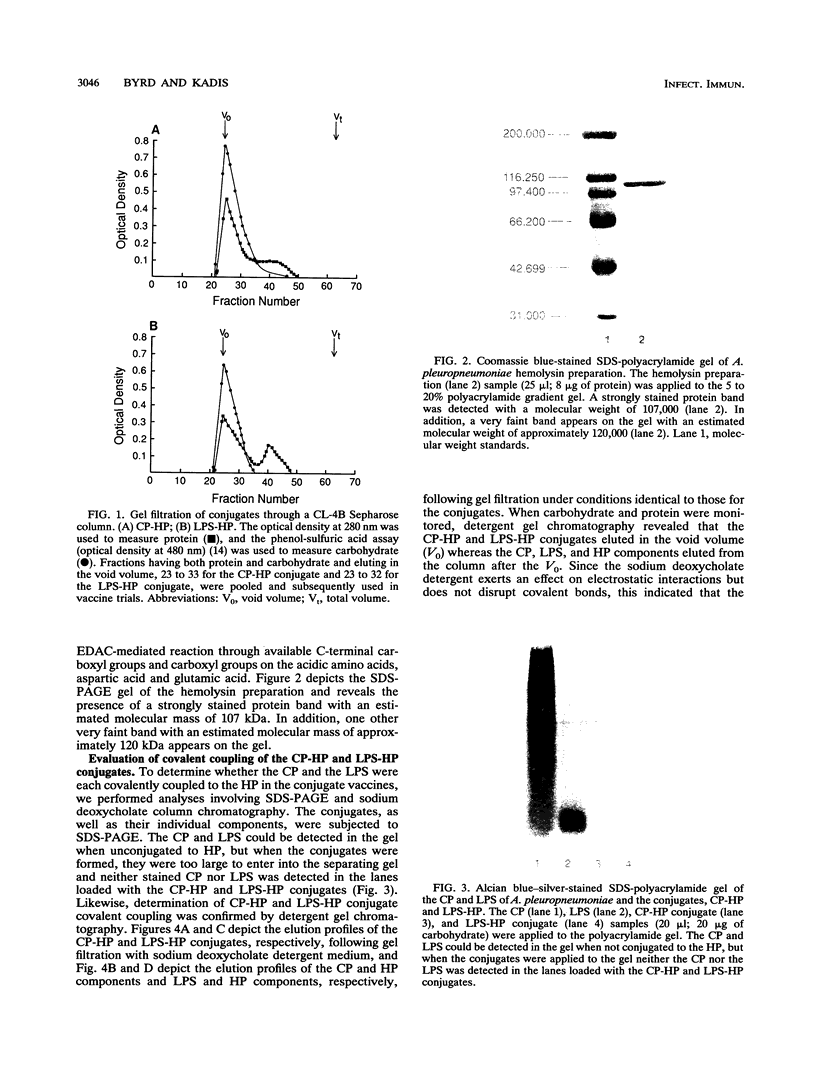
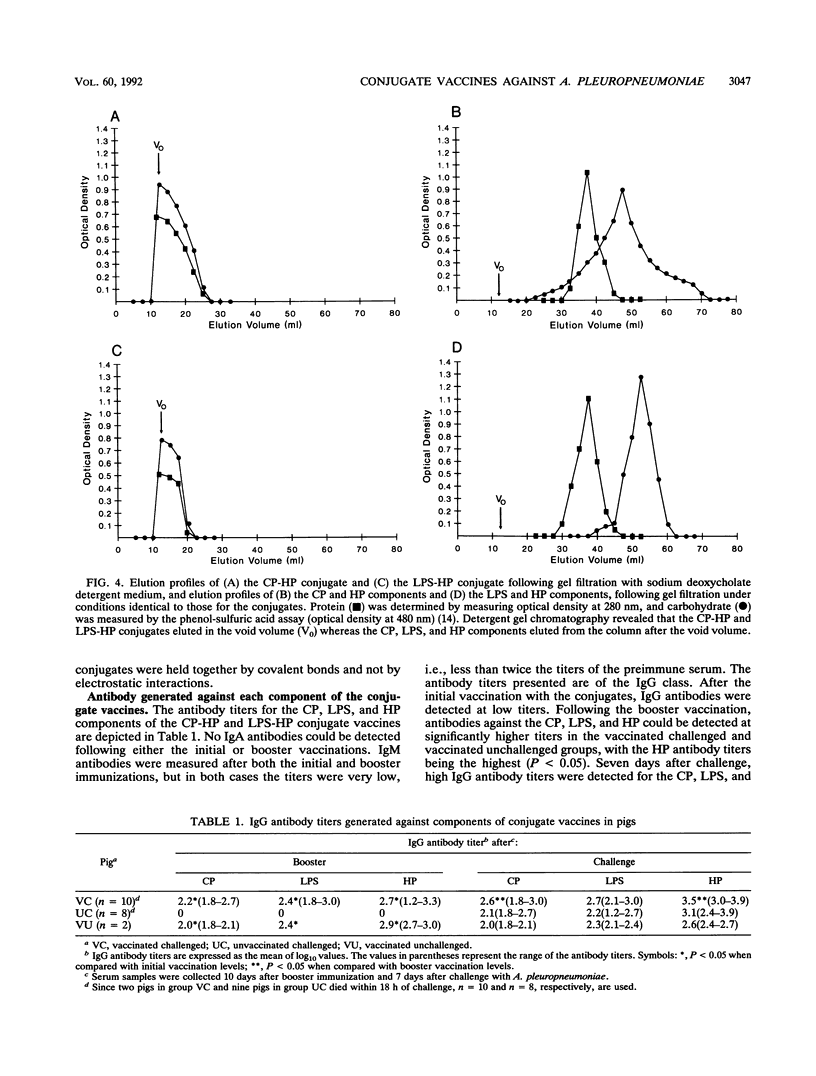
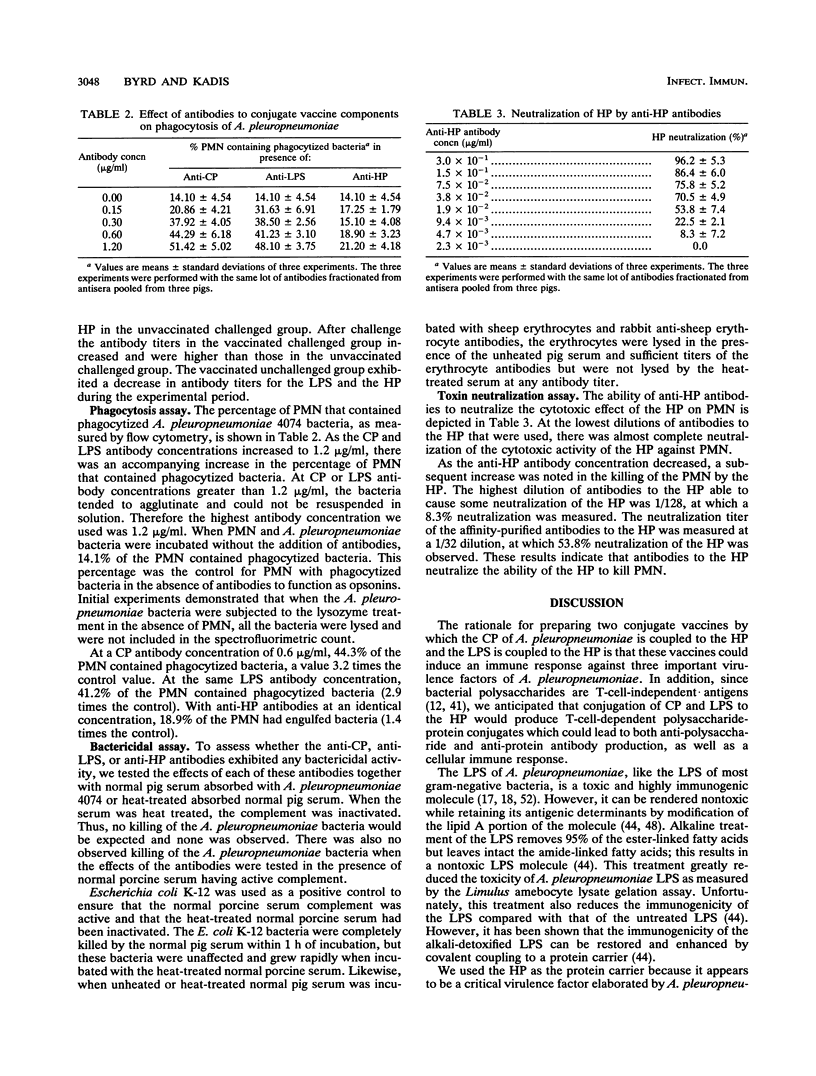



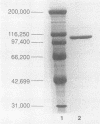
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlam C., Knights J. M., Mugridge A., Lindon J. C., Baker P. R., Beesley J. E., Spacey B., Craig G. R., Nagy L. K. Purification, characterization and immunological properties of the serotype-specific capsular polysaccharide of Pasteurella haemolytica (serotype A1) organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2415–2426. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen P. H., Shewen P. E., Rosendal S., Wilkie B. N. Toxicity of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae for porcine lung macrophages, peripheral blood monocytes, and testicular cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):673–676. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.673-676.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram T. A. Quantitative morphology of peracute pulmonary lesions in swine induced by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Vet Pathol. 1985 Nov;22(6):598–609. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Blau K., Inzana T. J., Nielsen K. H., Jacobson R. H., Corbeil R. R., Winter A. J. Killing of Brucella abortus by bovine serum. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3251–3261. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3251-3261.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneer H. G., Potter A. A. Effect of iron restriction on the outer membrane proteins of Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):798–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.798-804.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneer H. G., Potter A. A. Identification of a maltose-inducible major outer membrane protein in Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jun;6(6):425–432. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Rosendal S., Bossé J. T. Humoral antibody response and protective immunity in swine following immunization with the 104-kilodalton hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3829–3832. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3829-3832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Rosendal S., Bossé J. T., Wilkie B. N., Johnson R. Prevalence of seroreactors to the 104-kilodalton hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in swine herds. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):789–791. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.789-791.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Rosendal S., Johnson R., Hubler S. Immunoserological comparison of 104-kilodalton proteins associated with hemolysis and cytolysis in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Actinobacillus suis, Pasteurella haemolytica, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3210–3213. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3210-3213.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick W. E., Jr, Beurret M. Glycoconjugates of bacterial carbohydrate antigens. A survey and consideration of design and preparation factors. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1989;10:48–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly J. J., Deck R. R., Liu M. A. Immunogenicity of a Haemophilus influenzae polysaccharide-Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane protein complex conjugate vaccine. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3071–3079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorka-Cray P. J., Huether M. J., Stine D. L., Anderson G. A. Efficacy of a cell extract from Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae serotype 1 against disease in swine. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):358–365. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.358-365.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I. Immune responses to the lipopolysaccharides and capsular polysaccharides of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae in convalescent and immunized pigs. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.575-582.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Isolation and biological characterization of two lipopolysaccharides and a capsular-enriched polysaccharide preparation from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1433–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field T. R., Williams M. R., Bunch K. J. An improved method for the isolation of a neutrophil-rich fraction from porcine blood. Br Vet J. 1985 Jul-Aug;141(4):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0007-1935(85)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Fauci A. S., Green I., Frank M. M. A simple method for the determination of complement receptor-bearing mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):595–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Larivière S., Mittal K. R., Martineau G. P., Rousseau P., Cameron J. Evaluation of a Killed Vaccine Against Porcine Pleuropneumonia Due to Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can Vet J. 1985 Feb;26(2):86–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Mathison B. Serotype specificity and immunogenicity of the capsular polymer of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1580–1587. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1580-1587.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J. Purification and partial characterization of the capsular polymer of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1573–1579. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1573-1579.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C., Ashton F. E. Conjugation of meningococcal lipopolysaccharide R-type oligosaccharides to tetanus toxoid as route to a potential vaccine against group B Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):407–412. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.407-412.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. The serological properties of the cell surface proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2199–2206. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett A. D., Harrison L. R., Farrell R. L. Sequential study of lesion development in experimental haemophilus pleuropneumonia. Res Vet Sci. 1987 Mar;42(2):204–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley J. R., Kadis S. Growth and hemolysin production by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae cultivated in a chemically defined medium. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Oct;32(10):801–805. doi: 10.1139/m86-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley J. R., Kadis S., Mayberry W. R. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of a lipopolysaccharide from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.501-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H., Cowman M. K. Combined alcian blue and silver staining of glycosaminoglycans in polyacrylamide gels: application to electrophoretic analysis of molecular weight distribution. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jun;155(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. D., Whitlock R. H. Therapy of suspected septicemia in neonatal foals using plasma-containing antibodies to core lipopolysaccharide (LPS). J Vet Intern Med. 1987 Oct-Dec;1(4):175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.1987.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J., Paroz P., Krawinkler M., Baumgartner A. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, using an EDTA-extracted antigen for the serology of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Dec;42(12):2139–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Mandrup M. Pleuropneumonia in swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. A study of the epidemiology of the infection. Nord Vet Med. 1977 Nov;29(11):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Studies on the protection obtained by vaccination. Nord Vet Med. 1976 Jul-Aug;28(7-8):337–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pijoan C. Effect of Pasteurella multocida and Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae toxins on swine alveolar macrophages. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Sep;13(1-2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Schneerson R. Polysaccharide-protein conjugates: a new generation of vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):821–832. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Boyd D. A., Gilbride K. A. Comparative virulence of porcine Haemophilus bacteria. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Jan;49(1):68–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E., WHITE D. C., LEIDY G. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. II. STUDIES OF THE PATHOGENICITY OF THE ETIOLOGICAL AGENT, HEMOPHILUS PLEUROPNEUMONIAE. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:369–375. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford S. E., Josephson G. K. Porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia epizootic in southwestern Ontario: clinical, microbiological, pathological and some epidemiological findings. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Jan;45(1):2–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebunya T. N., Saunders J. R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jun 15;182(12):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W. The antimicrobial role of the neutrophil leukocyte. J Infect. 1981 Mar;3(1):3–17. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)92161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seid R. C., Jr, Sadoff J. C. Preparation and characterization of detoxified lipopolysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7305–7310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeze F. A., Latimer K. S., Kadis S. Role of haemophilus pleuropneumoniae lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in the pathogenesis of porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia. Am J Vet Res. 1987 May;48(5):768–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega M. V., Maheswaran S. K., Leininger J. R., Ames T. R. Adaptation of a colorimetric microtitration assay for quantifying Pasteurella haemolytica A1 leukotoxin and antileukotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Nov;48(11):1559–1564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vray B., Hoebeke J., Saint-Guillain M., Leloup R., Strosberg A. D. A new quantitative fluorimetric assay for phagocytosis of bacteria. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(2):147–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]