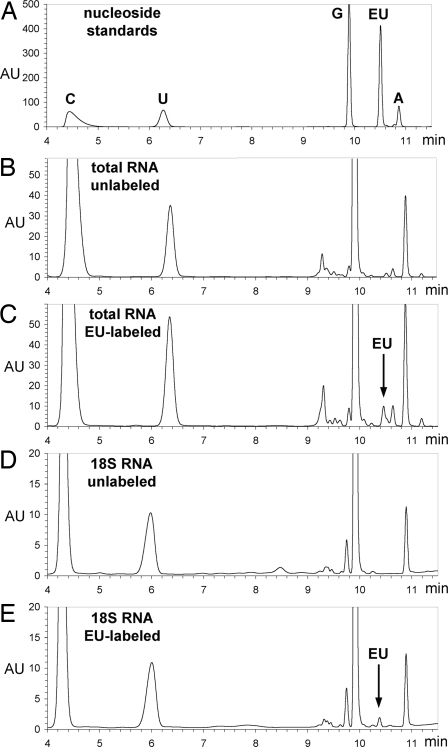
Fig. 3.
Analysis of EU incorporation into RNA. (A) HPLC separation of an equimolar mixture of pure cytidine, uridine, guanosine, EU, and adenosine. Absorbtion at 285 nm (in arbitrary units, AU) is plotted against elution time (in minutes). (B and C) HPLC analysis of nucleosides from total RNA isolated from unlabeled (B) and EU-labeled (C) cells. Note the EU peak in C, corresponding to a 2.8% substitution of uridine residues by EU. (D and E) HPLC analysis of nucleosides from unlabeled and EU-labeled, gel-purified 18S ribosomal RNA. The EU peak in E corresponds to a 1.3% substitution of uridine with EU. An identical degree of substitution was measured for the 28S ribosomal RNA (data not shown), consistent with the fact that 18S and 28S rRNAs are both derived from the pre-rRNA 45S precursor transcribed by RNA polymerase I.