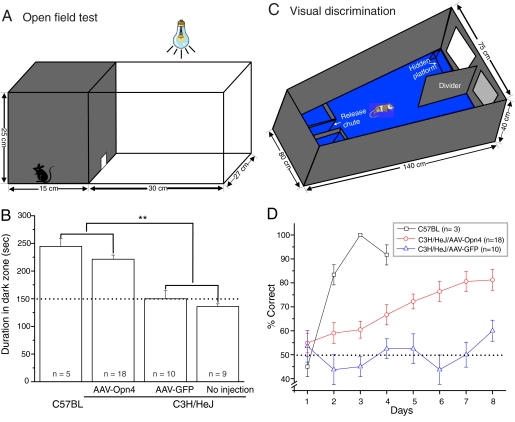
Fig. 4.
Enhancement of visual function in the AAV-Opn4 treated rd/rd mice. (A) The open-field test box consisted of a dark compartment (one third of the floor area) and a larger illuminated compartment (two thirds). A small opening located at floor level in the center of the dividing wall allowed mice to freely move between the lit and dark chambers. (B) Time spent in dark area by four groups of mice. The AAV-Opn4 treated rd/rd mice showed behavioral aversion to light: they spent significantly longer time in the dark chamber than their counterparts of either sham-injected or uninjected rd/rd mice (P < 0.01, t test). The exploratory behavior of uninjected C57BL mice is shown as comparison. Dotted line shows the behavior to be expected by chance. (C) Visual discrimination alley. Mice swam down a water-filled alley toward an illuminated or a dark target. The rewarded stimulus indicated the location of a submerged platform. (D) Melanopsin-treated (open circles) mice outperformed sham-injected (triangles) rd/rd mice in visual detection task over an 8-day trial (P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA test). Values represent mean ± SEM; n = number of mice.