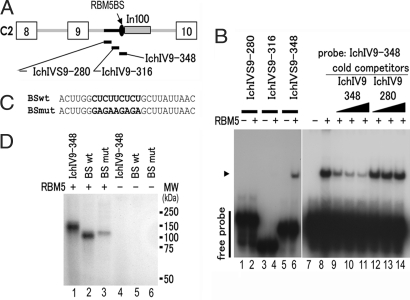
Fig. 5.
RBM5 binds to the U/C-rich intronic sequence immediately upstream of In100. (A) RNA oligomers corresponding to the RBM5-binding region in intron 9 of Casp-2. (B) The corresponding RNA oligomers were end-labeled with [γ-32]ATP and used in the gel-mobility shift assay as in shown Fig. 4. Only IchVS9-348 RNA forms a complex with the purified RBM5 protein. Cold IchIV9-348 RNA, but not IchIV9-280 RNA, competed for binding to RBM5. The arrowhead indicates the RNA–RBM5 complex. (C) RNA oligomers containing either the wild-type sequence (BSwt) or mutated RBM5-binding site (BSmut). (D) UV-cross-linking assay was performed by using end-labeled RNA oligomers in the presence (lanes 1–3) or absence (lanes 4–6) of the purified RBM5 protein. Compared with BSwt, BSmut showed significantly reduced interaction with RBM5.