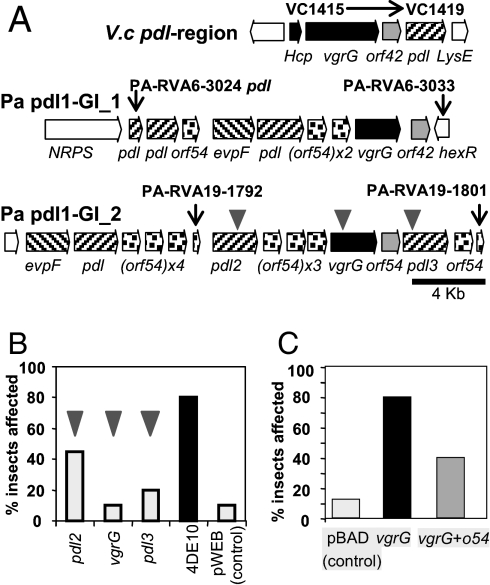
Fig. 4.
Putative novel virulence factors detected by RVA. (A) Comparison of a pdl operon in Vibrio cholerae O1 strain N16961 (Top) and two of the four pdl-o54 islands of P. asymbiotica ATCC43949. Homologous genes are coded by shading. Gray triangles represent transposon insertions in three individual genes for fine-scale mapping (see below). (B) Fine-scale mapping of the Pa pdl-GI_2 virulence island. The insertion mutants of the two pdl genes and the vgrG gene all show reduced toxicity when injected to G. mellonella, while the wild-type cosmid (4DE10) is fully toxic. Injection of control E. coli (pWEB cosmid) had negligible effect. (C) The vgrG toxin with or without the small flanking orf54 were cloned into the arabinose-inducible expression vector pBAD30. When induced, these clones were toxic by injection to G. mellonella. Interestingly, cloned orf54 reduced this effect suggesting its function is antagonistic to the toxic phenotype.