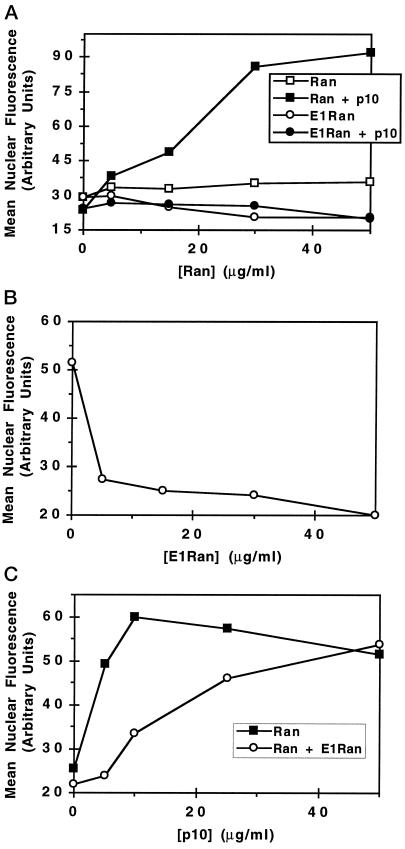
Figure 8.
Inhibition of import by E1-Ran can be overcome by the addition of excess p10. Assays were carried out at 21°C on permeabilized cells supplemented with 20 μg/ml human recombinant karyopherin α, 25 μg/ml human recombinant karyopherin β, 1 mM GTP, 20 μg/ml NLS-tagged, rhodamine-labeled human serum albumin, and the indicated concentrations of p10 and wild-type Ran·GDP or E1-Ran·GDP. Import was measured as mean nuclear fluorescence in arbitrary units. (A) Effect of p10 on wild-type Ran·GDP- and E1-Ran·GDP-mediated nuclear protein import. Assays were performed with the indicated amounts of wild-type Ran·GDP (▪, □) or E1-Ran·GDP (•, ○) in the presence (•, ▪) or absence (○, □) of 5 μg/ml p10. (B) Inhibition of nuclear protein import by E1-Ran. Assays were performed with (c 15 μg/ml wild-type Ran·GDP, 5 μg/ml p10, and the indicated concentrations of E1-Ran·GDP. (C) Effect of increasing concentrations of p10 on E1-Ran inhibition of nuclear protein import. Assays were performed with 15 μg/ml wild-type Ran·GDP in the presence (○) or absence (▪) of 30 μg/ml E1-Ran·GDP and the indicated concentrations of p10.