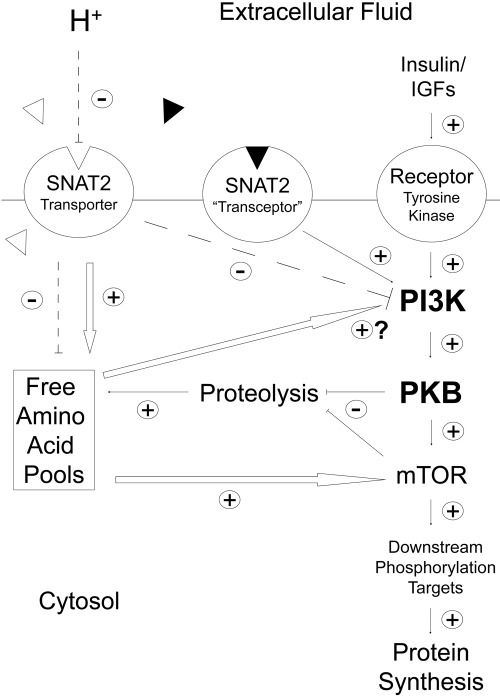
Figure 10.
Proposed scheme whereby the pH-sensitive SNAT2 amino acid transporter and the putative SNAT2/amino acid substrate “transceptor” complex influence amino acid signaling and global proteolysis in L6-G8C5 rat skeletal muscle cells. Dashed lines denote the inhibitory effect of low extracellular pH on the SNAT2 transporter and the resulting inhibition of PI3K and depletion of intracellular free amino acid pools. White arrows indicate known or suspected effects of amino acids whose intracellular concentrations are directly (e.g., L-Gln) or indirectly (e.g., L-Leu) regulated by SNAT2 transporter activity. ▵, Naturally occurring metabolizable amino acid substrates of SNAT2; ▴, synthetic nonmetabolizable SNAT2 substrate MeAIB.