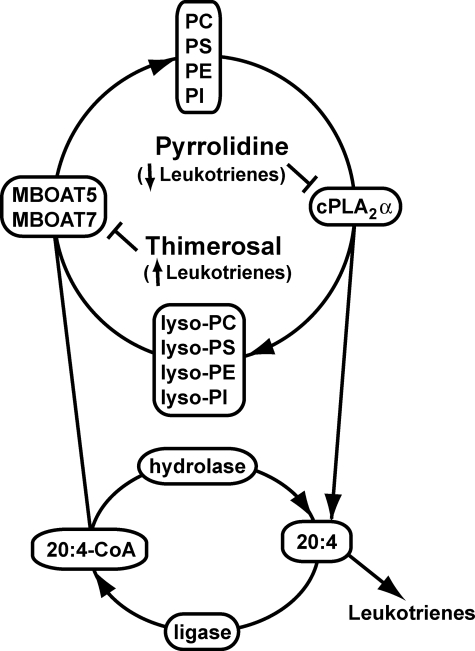
FIGURE 9.
Integrated model for phospholipid remodeling and arachidonic acid mobilization in human neutrophils. The major phospholipids in the human neutrophil are PC, PS, PE, and PI. Upon activation of the cell, 20:4 in the sn-2 position of these membrane lipids is released by the action of cPLA2α, generating the corresponding lysophospholipids and free 20:4. 20:4 can then be used for the production of various proinflammatory eicosanoid species (primarily LTB4) or can be returned to the phospholipid pool via the action of an acyl-CoA ligase and either MBOAT7 (that uses lyso-PI) or MBOAT5 (that uses lyso-PC, lyso-PS, and lyso-PE). Pyrrolidine, an inhibitor of cPLA2α, and thimerosal, an MBOAT inhibitor, decrease and increase, respectively, the production of eicosanoids, underscoring the importance of this deacylation/reacylation cycle in regulating the production of lipid-derived inflammatory mediators.