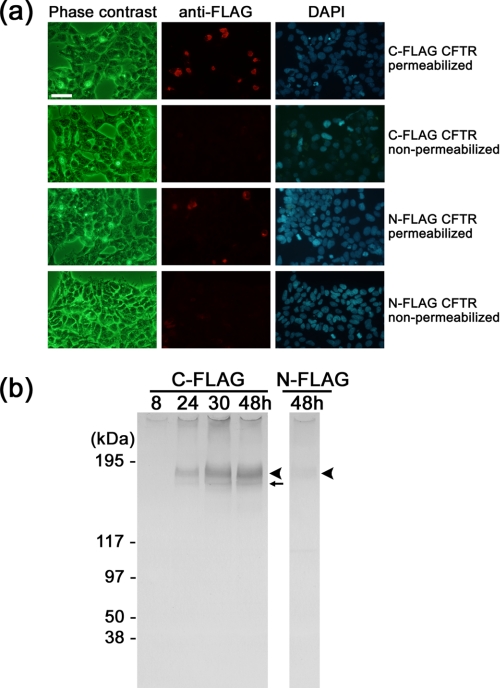
FIGURE 1.
Expression of recombinant CFTR in HEK cells. a, immunofluorescent images of HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-tagged CFTR. Top row, cells transfected with C-FLAG CFTR and permeabilized with 0.1% saponin. CFTR protein was detected using Cy3-conjugated anti-FLAG antibody (middle panel, red). Cell nuclei were visualized by 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)(right panel, blue). Second row, cells expressing C-FLAG CFTR were examined without saponin treatment. The cells were negative to the FLAG antibody, suggesting that the C-terminal epitope is inside the cell. Third row, cells transfected with N-FLAG CFTR and permeabilized by saponin. The level of Cy3 immunofluorescence is lower than that of C-FLAG CFTR. Fourth row, the non-permeabilized cells transfected with N-FLAG CFTR were also negative to the antibody. Cells were cultured for 48 h after transfection. The scale bar represents 50 μm. b, Western blot with anti-FLAG antibody. Left panel, cells were transfected with C-FLAG CFTR and cultured for the indicated periods. Proteins were solubilized from the membrane using DDM and precipitated with anti-FLAG gel. Expression of CFTR increased with the culture period up to 48 h. Right panel, the expression of N-FLAG CFTR was very low but was detected at the same size as C-FLAG CFTR. The broad bands at 177 kDa are glycosylated mature CFTR (arrowheads), and the sharp bands that move faster than the mature protein are core-glycosylated but immature CFTR (small arrow).