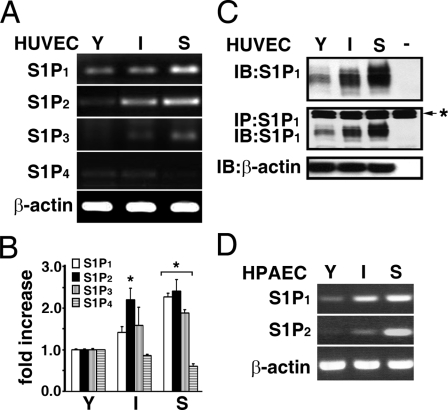
FIGURE 2.
Expression of S1P family receptor subtypes in ECs with different in vitro ages. The expression of S1P receptor subtypes in young, intermediate, and senescent HUVECs was measured by RT-PCR (A) and real-time qPCR (B) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” S1P1 expression was age-dependently increased in cultured HUVECs, and S1P2 expression was barely detected in young ECs, whereas it was markedly increased in intermediate and senescent ECs. Similarly, S1P3 was barely detected in young ECs and significantly up-regulated in senescent ECs. A low level of S1P4 receptor was detected in young and intermediate ECs and is absent in senescent ECs. S1P5 was not detected in ECs with different in vitro ages. The data are from a representative experiment, which was repeated six times with identical results. *, p < 0.01 (t test). C, endothelial extracts were immunoblotted (upper panel), or immunoprecipitated followed by Western-blotting with anti-S1P1 (middle panel). Immunoblotting with anti-β-actin was used as an internal control for loading (lower panel). The result is representative of triplicate experiments. -, assays were performed without endothelial extracts; *, immunoglobulin heavy chain used for immunoprecipitation assays. D, S1P1 and S1P2 expression in HPAECs with different in vitro ages. S1P1 expression was age-dependently increased in HPAECs. Also, S1P2 expression was significantly induced in senescent HPAECs and was undetected in young HPAECs.