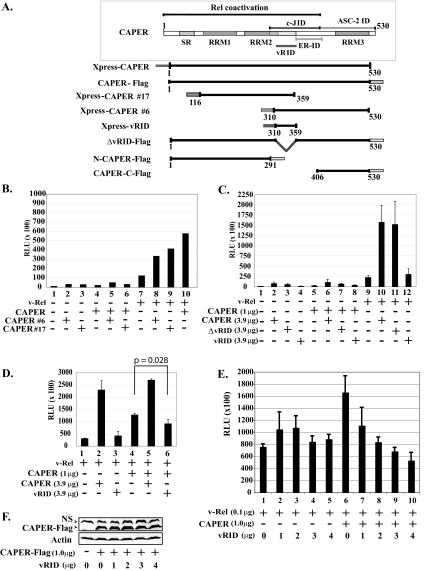
FIG. 4.
CAPERα sequences important for coactivation with v-Rel. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type CAPERα and mutants. SR, serine-arginine-rich region; RRM, RNA recognition motif; c-JID, c-Jun interaction domain; ER-ID, estrogen receptor interaction domain; ASC-2 ID, ASC-2 interaction domain; vRID, putative v-Rel interaction domain. (B) CAPERα fragments 6 and 17 synergize v-Rel-mediated activation. Luciferase assays were carried out as for Fig. 3A with extracts from 293T cells cotransfected with v-Rel (0.1 μg) alone or together with CAPERα (1.0 μg) and/or CAPERα fragments (no. 6 or 17) (3.9 μg) and an IL-6κB-luciferase reporter (1.0 μg) and hRL-null Renilla control (0.01 μg). The averages from three experiments are shown. (C) Like CAPERα, CAPERα mutant ΔvRID synergizes v-Rel-mediated activation, in contrast to vRID. Luciferase assays were carried out as for panel B with CAPERα mutants (ΔvRID or vRID). (D) vRID acts in a dominant-negative fashion. Luciferase assays were carried out as for panel B with extracts from cells cotransfected with v-Rel (0.1 μg) alone or together with CAPERα (1.0 μg) alone or together with excess CAPERα or vRID (3.9 μg). (E) Transfection of increasing amounts of vRID leads to dose-dependent inhibition of CAPER-mediated coactivation of v-Rel. Cells were cotransfected with v-Rel (0.1 μg) alone or together with CAPERα (1 μg) along with increasing amounts of vRID (0 to 4 μg). (F) Western blot showing that transfection of increasing amounts of vRID does not alter the levels of CAPERα-Flag. NS, nonspecific band.