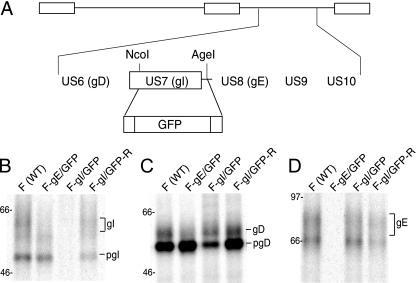
FIG. 3.
Construction and characterization of an HSV gI− mutant. (A) Schematic of the HSV unique short component, including the US6 to US10 genes. In F-gI/GFP, the gI (US7) coding sequences between NcoI and AgeI restriction sites were replaced with GFP sequences. A second virus, in which gI sequences were repaired, was produced by cotransfecting Vero cells with F-gI/GFP DNA and a plasmid containing the gE and gI genes. (B to D) R970 cells were infected with either wild-type HSV (WT), F- gE/GFP, F-gI/GFP, or F-gI/GFP-R using 10 PFU/cell for 6 h, and the cells were labeled with [35S]methionine/cysteine for 3 h. gI (B), gD (C), and gE (D) were immunoprecipitated from detergent extracts of the cells using MAb 3104, 3114, or DL6, respectively, and gel electrophoresis was performed. The positions of mature glycoproteins, gI, gD, and gE, and immature forms of glycoproteins, pgI and pgD, and marker proteins of 97, 66, and 46 kDa are indicated.