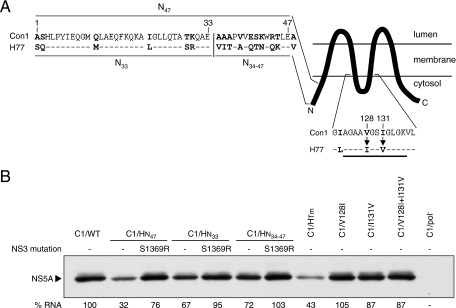
FIG. 8.
Dissection of the H77-derived sequences in the N-terminal and transmembrane domains of NS4B that are detrimental for Con1 RNA replication. (A) A cartoon schematic of the predicted topology of NS4B (TMHMM; www.cbs.dtu.dk), showing the N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic domains flanking the larger transmembrane domain. The first 48 amino acids of H77 and Con1 NS4B are aligned on the upper left with divergent residues in boldface. The vertical line shows the division of the N terminus into the first 33 amino acids (C1/HN33) and residues 34 to 47 (C1/HN34-47). Shown below is a comparison of H77 and Con1 NS4B sequences between residues 122 and 137 of NS4B. The proposed cytosolic loop is underlined, amino acid differences are shown in boldface, and arrows denote the amino acid substitutions tested. (B) At 96 h posttransfection, NS5A protein expression was visualized by Western blotting and the number of HCV RNA molecules in 1 μg of total cellular RNA was quantified by real-time RT-PCR. Below the NS5A blot, HCV RNA levels (% RNA) are shown as percentages of the C1/WT level, which has been set at 100%. The HCV RNA levels are presented as the mean RNA level from two independent experiments with an average standard deviation of ±5%.