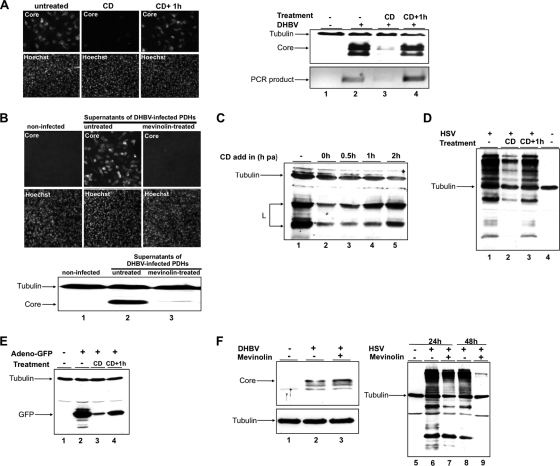
FIG. 2.
Cellular cholesterol is dispensable for DHBV infection. (A) PDHs were pretreated with CD. Thereafter, cultures were infected with DHBV in the presence (CD) or 1 h after removal of the drug (CD+1h). Cells were maintained for a further 3 days in medium devoid of drugs and virus, harvested, and subjected to immunofluorescence (left panel) and immunoblot analysis for core protein and to PCR for viral DNA (right panel). (B) Congenitally DHBV-infected PDHs were treated or not with mevinolin, and supernatants were harvested. Infectivity of virus progeny in the supernatants was tested by immunofluorescence (upper panel) and immunoblot (lower panel) analysis for core protein. (C) After DHBV attachment at 4°C and removal of unbound inoculum, PDHs were treated with CD at indicated time points at 37°C. The lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for L; tubulin served as a loading control. (D and E) PDHs were treated, infected with HSV or a recombinant adenovirus encoding GFP, harvested, and analyzed by immunoblotting for HSV and GFP, respectively. Tubulin served as a loading control. (F) PDHs were treated with mevinolin to inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis prior to DHBV infection. To control the extent of cholesterol depletion by mevinolin treatment, PDHs were infected with HSV 24 h and 48 h after inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis. Immunoblots for DHBV core (left panel) and HSV (right panel) were performed. Tubulin served as a loading control. h pa, hour postattachment.