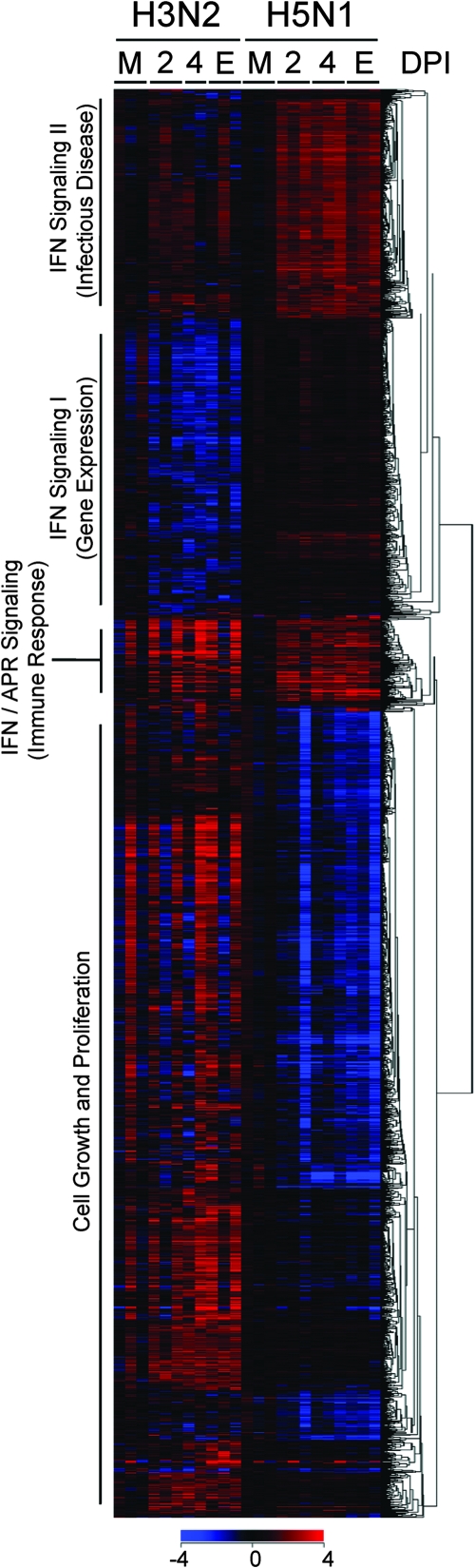
FIG. 1.
Four prominent gene expression clusters identified in H3N2- and H5N1-infected ferrets. Sequential Student's t tests (time point versus mock) identified genes significantly differentially expressed (P ≤ 0.05 and ≥2-fold change) for at least one time point and group during H3N2 and H5N1 infection in ferrets. These genes were combined with significantly differentially expressed genes (≥2-fold change for at least one time point and group and P ≤ 0.05) identified by EDGE analysis of differential gene expression between H3N2- and H5N1-infected ferrets. As shown, 2,295 significantly different genes were analyzed by one-way (by gene) hierarchical clustering (red, upregulated; blue, downregulated). The most significant signaling pathway(s) (IFN and IFN/acute-phase response signaling) or network (cell growth and proliferation, gene expression, immune response, and infectious disease) according to IPA for the resulting clusters are noted. M, mock. E, end point as described in Materials and Methods.