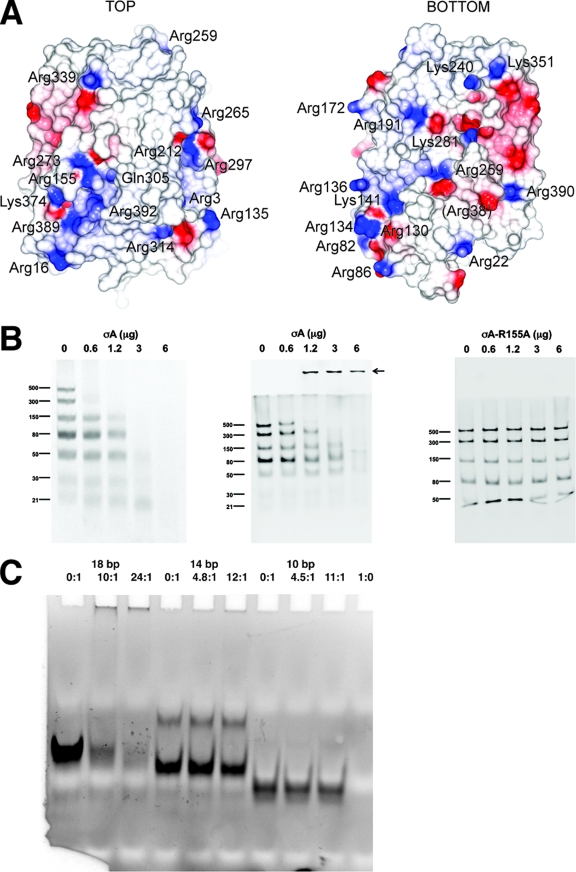
FIG. 3.
dsRNA binding of the σA protein. (A) Electrostatic surface of σA. On the left the orientation is as in Fig. 1A; on the right the view has been rotated 180° around a vertical axis centered on the apex. Positively charged residues on the molecular surface are labeled. The location of Gln305 is also shown, whereas Arg38 is shown in parentheses, as it is barely surface exposed. (B) dsRNA gel shift assays. The assays were performed using σA at 0.6 mg/ml in TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 1 mM EDTA) and a dsRNA ladder which contains seven types of dsRNA of different lengths (500, 300, 150, 80, 50, 30, and 21 bp) at 0.5 mg/ml. Increasing amounts of σA (0, 0.6, 1.2, 3.0, and 6.0 μg) were incubated with 0.5 μg of dsRNA ladder in TE buffer-150 mM NaCl for 10 min on ice. Then, samples were analyzed by nondenaturing gel electrophoresis. (Left) A 10% polyacrylamide gel in TBE buffer was used. (Middle and right) Discontinuous gels as described by Laemmli (22) were used, with a 10% polyacrylamide separating gel and omission of sodium dodecyl sulfate from the sample, the gel, and the running buffer (13). Nonmutated σA protein was used in the left and middle panels. The right panel shows a gel shift assay performed with the Arg155-to-Ala mutant. Identical results were obtained with the Arg273-to-Ala mutant (data not shown). An arrow in the middle panel indicates the high-molecular-weight complexes observed. (C) Binding of σA to small dsRNA fragments as observed by gel shift assay. In the first three lanes an 18-bp dsRNA was used, in the next three lanes a 14-bp dsRNA was used, and in lanes 7 to 9 a 10-bp dsRNA was used. In lane 10 σA alone was loaded. σA/dsRNA ratios are indicated above the lanes.