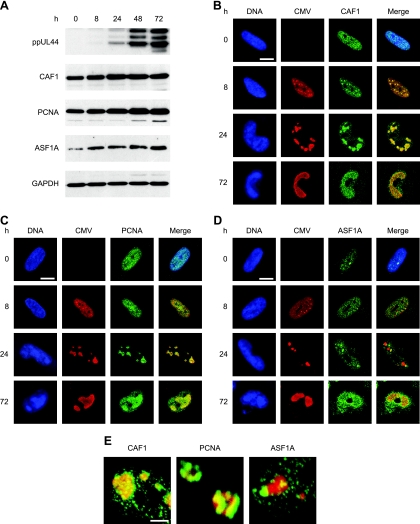
FIG. 6.
Increased accumulation of human nucleosome assembly proteins and association with intranuclear viral replication compartments during CMV infection. (A) MRC-5 cells were mock infected (0 h) or infected with CMV for 8 to 72 h, as indicated, and proteins from whole-cell extracts were separated in 10% polyacrylamide-SDS gels. After Western blot transfer, the proteins were reacted with the respective antibodies as shown in Table 2. (B to D) Mock- or CMV-infected MRC-5 cells were fixed and permeabilized with paraformaldehyde/methanol (B and C) or paraformaldehyde/Triton X-100 (D) at the indicated time points and incubated with primary antibodies specifically detecting the CMV IE2 (0 and 8 h) or ppUL44 (24 and 72 h) proteins, together with antibodies directed against CAF1 p48, PCNA, or ASF1A, as indicated. Samples were subsequently stained with an Alexa Fluor 594 conjugate, an Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate, and DRAQ5. Single- and dual-color merge confocal images of representative nuclei are shown. Scale bars, 10 μm. (E) Three-dimensional projections of z stacks showing details of the spatial relationship between CMV replication compartments (ppUL44) (red) and complexes containing the indicated cellular chromatin assembly proteins (green) at 24 h postinfection. The frames were acquired with a step width of 0.38 μM and rendered with the Zeiss LSM510 software. Scale bar, 1 μm.