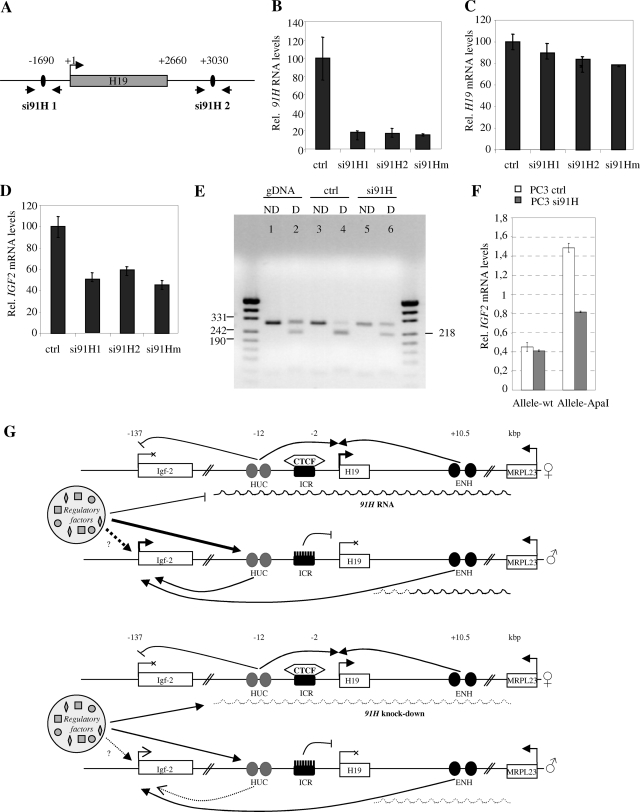
FIG. 8.
91H silencing by RNA interference reduces IGF2 expression on the paternal allele. (A) Map of H19 region indicating the positions of siRNA sequences and the PCR primer pairs used in real-time PCR. T47D cells were transfected with siRNA targeting either the green fluorescent protein (ctrl) or the 91H RNA (si91H 1 and 2 alone or in combination). 91H (B), H19 (C), and IGF2 (D) RNA levels were determined by real-time RT-PCR 24 h after transfection. The results were normalized to RPLP0 expression levels. (E) PC3 cells were transfected with si91H, and the imprinting status of the IGF2 alleles was examined using a RT-PCR amplification digested (D) or undigested (ND) with an ApaI polymorphic restriction site available in this cell line. (F) The IGF2 expression levels were determined on each parental allele using an allele-specific RT-PCR amplification method (51) from PC3 cells transfected with control siRNA or with si91H. (G) Model for 91H trans effect on IGF2 expression. Two sets of enhancers (HUC and ENH sequences) regulate IGF2 expression. Both would be required for full expression of the gene. In addition, the two IGF2 alleles would be competing for a common limited stock of regulatory elements (methylation/acetylation/transcription?). On the maternal allele, 91H would block the locus and prevent the HUC sequences from interaction with any regulatory factors. These would be then directed on the paternal allele, in the HUC region, and/or in the IGF2 promoter region and would cooperate with the cis endodermic enhancers, resulting in IGF2 enhanced expression. Upon siRNA treatment and 91H knockdown, the competition would be lost and, as a consequence, both IGF2 alleles would be now able to interact with the regulatory factors with similar efficiencies. Because these factors are in a limiting amount, a part would be depleted from the paternal IGF2 allele to interact with the maternal allele. This would lead to a paternal IGF2 expression decrease but unchanged maternal IGF2 expression because of the absence of functional ENH sequences. Arrows indicates positive regulations, whereas lines with bars correspond to inhibitions.