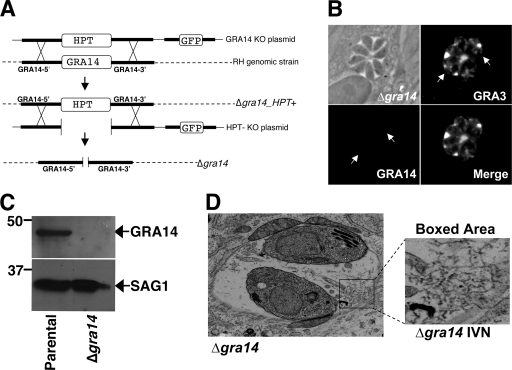
FIG. 3.
Targeted disruption of the gene encoding GRA14. (A) Schematic depicting the GRA14 knockout strategy. Using homologous recombination, the GRA14 coding region was replaced with the selectable marker HPT. After the generation of ΔGRA14_HPT+ clonal parasites, the HPT marker was removed by a second round of homologous recombination to generate the Δgra14strain. (B) IFA of cells infected with Δgra14 parasites does not show staining with GRA14 polyclonal antiserum (the arrows indicate the positions of the vacuole) but does show GRA3 staining in the PV (positive control). (C) Western blot analysis of parental and Δgra14 parasite lysates showing that GRA14 is not present in Δgra14 lysates. SAG1 was used as a loading control. (D) Using transmission electron microscopy, Δgra14 parasites were analyzed for ultrastructural defects in the PV. No gross changes in the IVN structure (boxed area), PVM morphology, or host organelle association were observed.