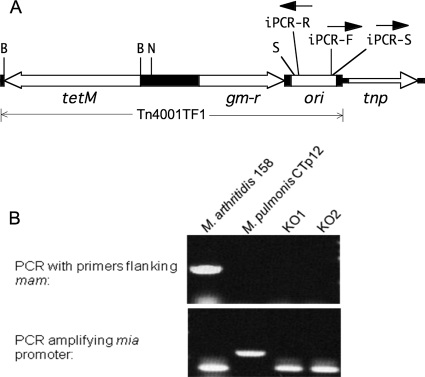
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic of plasmid pTF85 illustrating transposon Tn4001TF1 with the direction of transcription of the genes (open bars) indicated by arrows. tetM, tetracycline resistance marker; gm-r, gentamicin resistance marker; tnp, transposase gene; ori, origin of plasmid replication; B, BamHI restriction site; N, NotI site into which the mia-mam gene was inserted for overexpression studies; S, rightmost Sau3A1 site in Tn4001TF1 (other Sau3A1 sites not shown). The orientations of primers iPCR-F, iPCR-R, and iPCR-S used for inverse PCR to map the genomic location of the transposon are indicated. (B) Agarose gel of direct PCR products obtained from amplification of genomic DNA isolated from the mam knockout mutants KO1 and KO2 and using the mam-F-Eco and mam-R-Not primers that flank mam. Genomic DNA from wild-type M. arthritidis 158 and M. pulmonis strain CTp12 was used as positive and negative control, respectively. PCRs amplifying the mia promoter with primers mia-PF-Not and mia-PR-Eco were performed to serve as quality controls of DNA template preparation. The direct PCR products of the mam gene and the mia promoter are 805 bp and 369 bp, respectively.