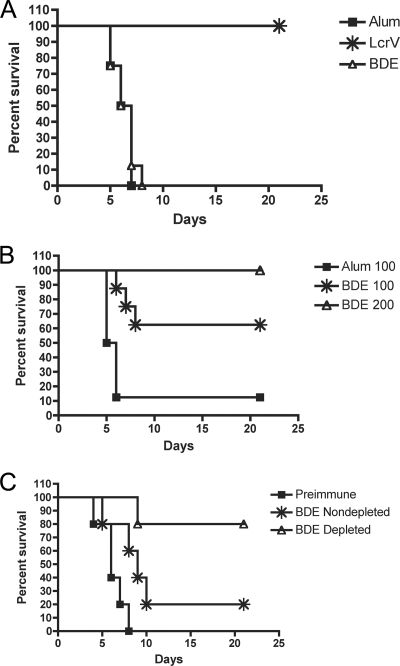
FIG. 4.
Passive immunization of naïve mice with anti-LcrV or anti-BDE serum. Naïve BALB/c mice were infected i.v. with a lethal dose of F1− Y. pestis. Passive immunization was performed by i.p. injection of doses of pooled anti-LcrV, anti-BDE, or control (alum or preimmune) sera. Mouse survival was recorded for 21 days. (A) Mice (n = 8 per group) were injected with a single dose (100 μl) of sera on day +1 relative to infection. (B) Mice were injected with three doses of sera (100 μl or 200 μl in each dose) on days −1, 0, and +1. The difference in the survival curves was significant (BDE at 100 μl versus alum at 100 μl, P < 0.05) as determined by a log rank test. For BDE at 100 μl and alum at 100 μl, n = 8; for BDE at 200 μl, n = 4. (C) Mice (n = 5 per group) were injected with three doses of sera (100 μl in each dose) on days −1, 0, and +1. BDE-depleted sera were exposed to LcrV-coated beads to remove anti-LcrV antibody prior to use for passive immunization. The difference in the survival curves was significant (non-BDE depleted versus preimmune, P < 0.05; BDE depleted versus preimmune, P < 0.05) as determined by a log rank test.