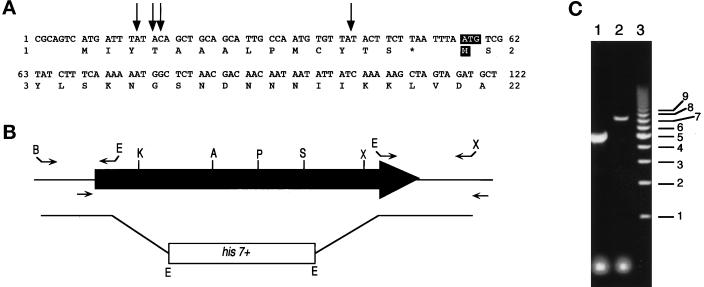
Figure 4.
Cloning 5′ of myp2+ and construction of the myp2-disrupted strain. (A) The DNA sequence for the 5′ region of myp2+ in the pmyp2BS construct is shown along with the deduced amino acid sequence. The arrows indicate the position of the beginning of four separate 5′ RACE PCR products that were sequenced. The putative start codon and methionine are highlighted with white lettering against black. (B) Schematic representation of the genomic locus of myp2+. The shaded arrow represents the open reading frame of 6312 bp. The primers used to amplify the 5′ and 3′ regions of myp2+ that were used to generate the knockout construct are represented above the locus. The restriction sites used to ligate together the knockout construct are indicated at the ends of the primers. B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; X, XhoI. The primers used to amplify the genomic locus from His+ haploids generated from the diploid transformed with the knockout construct are indicated below the locus. (C) Amplification of the genomic locus by colony PCR from His+ haploids. PCR products were separated on an 0.8% agarose gel. Lane 1 represents a homologous recombination event resulting in disruption of the myp2+ locus by his7+. The disrupted locus is 2.5 kb smaller than the wild-type locus. Lane 2 represents a heterologous recombination event in which his7+ has been integrated elsewhere in the genome thus leaving the myp2+ locus intact. Lane 3 is the molecular weight marker with sizes in kilobases indicated to the right.