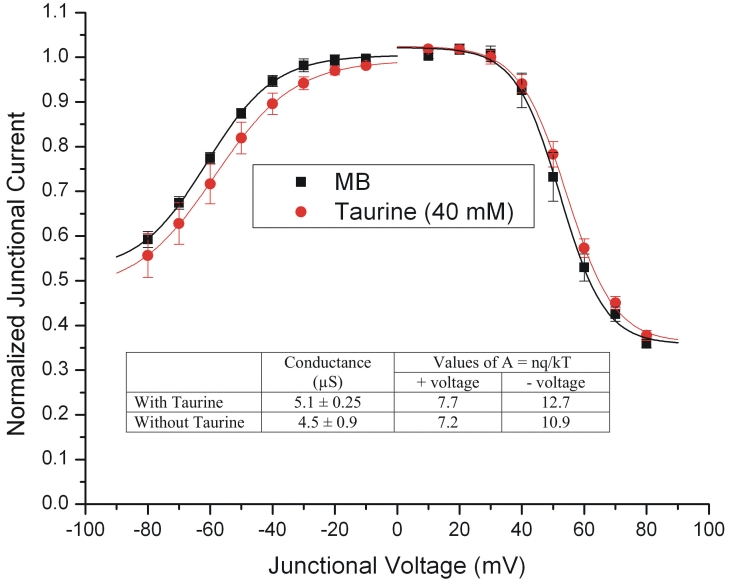
Figure 6.
Taurine effect on junctional conductance. Exposure to 40 mM taurine had no significant effect on the voltage sensitivity of the junctional currents recorded over the range of ±80 mV, although there was a slight current reduction at negative junctional voltages. The data (n=4 for each condition) were fit by the Boltzmann equation: Gjss = { (Gjmax – Gjmin ) / ( 1 + exp [A ( Vj –Vo ) ] } + Gjmin where Gjmax (normalized to unity) is the maximum conductance, Gjmin is the residual conductance at large values of Vj, and Vo is the Vj at which Gjss = (Gjmax–Gjmin)/2. The constant A (A=nq/kT) represents the voltage sensitivity in terms of gating charge as the equivalent number (n) of electron charges (q) moving through the membrane, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the absolute temperature. As shown in the inset, taurine had no significant effect on the junctional conductance between paired oocytes expressing this gap-junctional protein (p=0.5444 by Student’s t-test), and there were no significant differences in the values of A for taurine treated and control oocytes in either the positive or negative branches of the curves. These findings are a good indication that taurine does not affect Cx43 gap junctional channels.